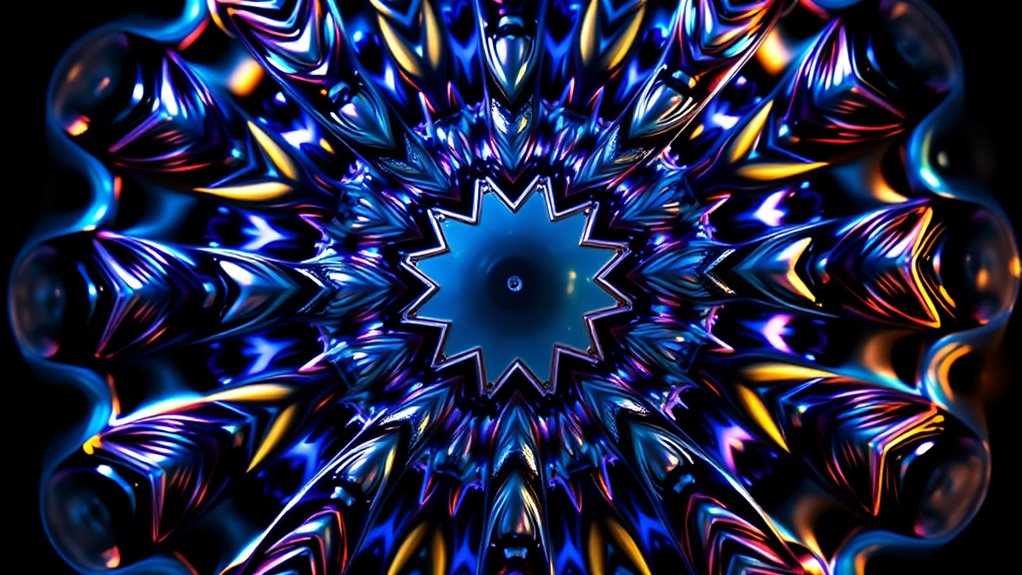
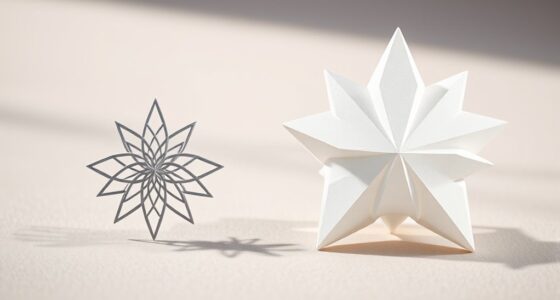
Rotation and reflection symmetry showcase the beauty of motion and mirror images in both nature and art. When shapes look the same after turning or flipping, they create a sense of harmony, stability, and balance. These types of symmetry reveal how natural forms and human designs can be both dynamic and calming. Exploring how symmetry works can discover a deeper appreciation for the patterns that make our world so visually appealing and intriguing. If you explore further, you’ll discover even more about this fascinating harmony.
Key Takeaways
- Rotation symmetry gives shapes the appearance of motion when turned around a center point.
- Reflection symmetry creates balanced, mirror-image patterns that evoke harmony and stability.
- Both symmetries are evident in natural forms like flowers, shells, and animal markings.
- Artistic designs utilize symmetry to produce lively, balanced, and visually appealing patterns.
- Recognizing symmetry enhances appreciation of natural beauty and the dynamic qualities of design.
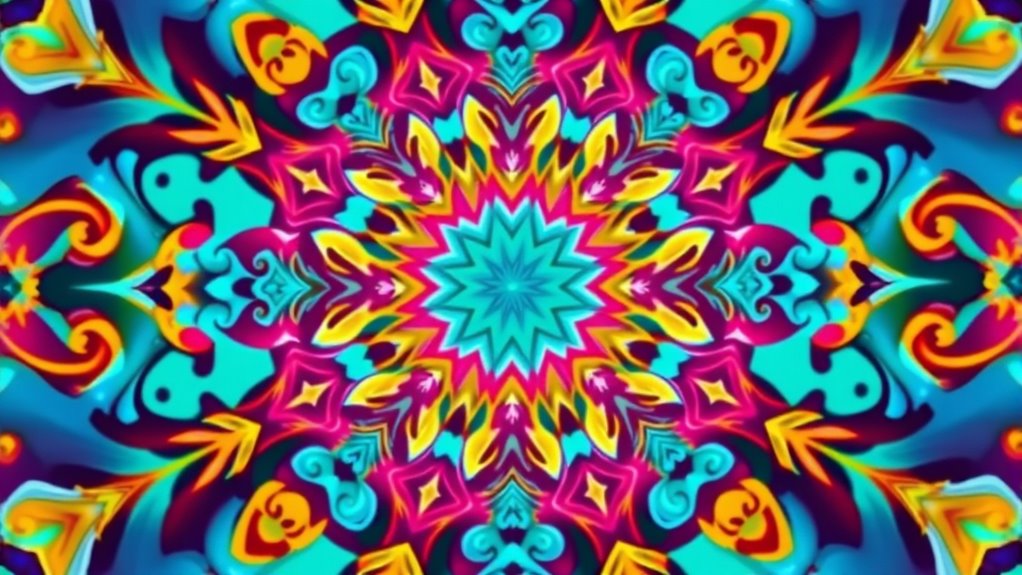

Have you ever wondered what makes a shape look the same after turning or flipping? It’s a fascinating concept called symmetry, specifically rotation and reflection symmetry. When you look at nature, you’ll notice countless examples of these patterns in nature—flowers, shells, snowflakes—each showcasing how symmetry creates harmony and balance. These patterns aren’t just beautiful; they reveal the underlying order in the natural world. You might also see symmetry in artistic applications, where artists deliberately incorporate it to evoke feelings of stability, beauty, and rhythm. Whether in architecture, design, or painting, symmetry adds a pleasing structure that guides your eye and creates a sense of unity.
Symmetry in nature and art creates harmony, balance, and visual appeal across countless patterns and designs.
When you consider rotation symmetry, you realize that some shapes look exactly the same after turning around a central point. Think of a starfish or a mandala; these objects maintain their appearance even when rotated by certain angles. This type of symmetry is often used in decorative arts because it provides a sense of motion and continuity. In nature, rotation symmetry helps animals and plants develop complex yet balanced forms. For example, many flowers display radial symmetry, where a rotation by a specific degree—such as 60 or 120 degrees—leaves the flower looking the same. In artistic applications, artists exploit this property to design patterns that seem lively and dynamic, yet perfectly balanced.
Reflection symmetry, on the other hand, occurs when one half of a shape mirrors the other across a line—called the line of symmetry. Think of butterflies, leaves, or human faces; each exhibits a mirror image that creates a sense of harmony and proportion. In nature, reflection symmetry often appears in the way animals are patterned or in the structure of certain crystals. When you see artwork or architecture that employs reflection symmetry, it’s not just about aesthetics; it’s about creating a feeling of stability and order. Artists often use reflection symmetry to evoke calmness or to emphasize balance, reinforcing the natural tendency for humans to find symmetry pleasing.
Understanding how shapes can look the same after rotation or reflection helps you appreciate the beauty and functionality of symmetry in both nature and art. Recognizing these patterns in nature fosters a deeper connection to the world around you, revealing how natural forms employ symmetry to thrive and adapt. Additionally, biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining these natural patterns and structures, ensuring the resilience of ecosystems. Meanwhile, in artistic applications, symmetry allows creators to craft visually compelling works that resonate with viewers, offering a sense of familiarity and comfort. Whether you’re admiring a snowflake or examining a well-designed building, symmetry’s motion and balance are what make shapes intriguing and meaningful. It’s a universal language of beauty that continues to inspire and fascinate across disciplines and cultures.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Symmetry Operations Relate to Real-World Art and Architecture?
Symmetry operations play a key role in shaping artistic patterns and enhancing architectural aesthetics. When you observe designs with rotational or reflective symmetry, you see how these operations create harmony and balance. Artists and architects use symmetry to evoke beauty and order, making structures and patterns more engaging and pleasing. By applying symmetry principles, you can appreciate how motion and repetition contribute to the visual appeal and structural integrity of art and architecture.
Can Objects Have Both Rotational and Reflection Symmetry Simultaneously?
Sure, your everyday objects can have both rotational and reflection symmetry, showcasing the magic of dual symmetry through combined transformations. Imagine a snowflake or a butterfly—these beauties display both types, proving symmetry isn’t just for math geeks. By combining rotations and reflections, you create objects with intricate, harmonious patterns that catch your eye and challenge your perception, making the world around you a stunning showcase of dual symmetry in action.
How Do Symmetry Groups Help in Understanding Molecular Structures?
Symmetry groups help you understand molecular structures through group theory, which categorizes all possible symmetries in a molecule. By analyzing molecular geometry, you can identify the symmetry elements and classify the molecule into a specific symmetry group. This simplifies predicting physical and chemical properties, such as polarity and reactivity. Fundamentally, symmetry groups give you a systematic way to study and compare molecular shapes, making complex structures more manageable.
Are There Natural Examples of Objects With Perfect Rotational Symmetry?
Yes, there are natural examples of objects with perfect rotational symmetry. You might notice this in biological structures like starfish, which have fivefold symmetry, or in some flowers and snowflakes that display sixfold or more. These natural patterns often exhibit beautiful, precise rotational symmetry, helping organisms optimize functions like movement or structural stability. Recognizing these patterns reveals how symmetry guides the design and function of many natural objects around you.
How Does Symmetry Influence the Design of Mechanical Parts?
Honestly, if you want your mechanical parts to look like they belong in a sci-fi movie, symmetry is your best friend. It provides aesthetic balance, making designs pleasing to the eye, and guarantees structural stability, so your gadgets don’t fall apart at the first bump. Symmetry simplifies manufacturing, reduces weaknesses, and helps parts fit together seamlessly. Basically, it’s the secret sauce for making your machines both beautiful and durable.
Conclusion
As you explore rotation and reflection symmetry, remember they’re like life’s dance moves—showing how everything can change yet stay beautifully the same. These patterns are symbols of balance and harmony, reminding you that even in motion, there’s stability. Embrace the swirling rotations and mirrored reflections, for they reveal the hidden poetry in everyday objects. Just like life’s twists and turns, these symmetries teach you that beauty lies in the seamless flow of change.