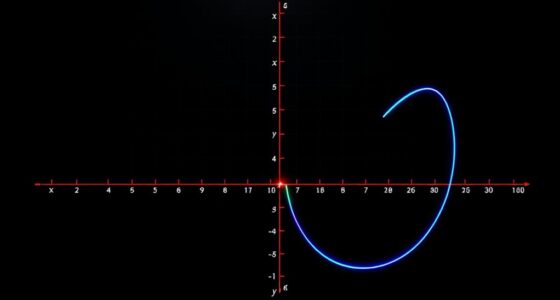
To master geometric transformations, focus on understanding how to manipulate figures using translation, scaling, and rotation matrices within coordinate systems. These tools let you precisely shift, size, or turn shapes in 2D or 3D space. By combining matrices, you can perform complex moves efficiently. Fully grasping these concepts enables you to confidently modify figures and visualize their changes. Keep exploring, and you’ll discover how these transformations unleash endless creative possibilities.
Key Takeaways
- Understand different types of transformations: translation, scaling, rotation, and their corresponding matrices.
- Learn how to set up and interpret coordinate systems for accurate transformation application.
- Master matrix multiplication to combine multiple transformations efficiently.
- Practice applying transformation matrices to points and shapes for desired modifications.
- Use visualization tools to observe and analyze the effects of transformations on figures.

Geometric transformations are fundamental tools that allow you to manipulate and modify shapes and figures in a plane or space. When you understand how these transformations work, you gain the ability to change an object’s position, size, or orientation with precision. One of the key concepts in mastering these transformations involves coordinate systems, which serve as the framework for describing points and shapes mathematically. Whether you’re working in Cartesian coordinates or other systems, understanding how points are represented provides the foundation for applying transformations effectively. Additionally, familiarity with transformation matrices enables systematic and efficient manipulation of objects in various dimensions. transformation matrices are essential tools that enable you to perform complex transformations systematically. These matrices act as operators that, when multiplied by coordinate vectors, produce new coordinates for the transformed shape. For example, a simple translation shifts every point of an object by a fixed amount, and this can be represented using a translation matrix that, when applied to each point’s coordinates, moves the shape to a new location. Similarly, scaling matrices modify the size of objects by stretching or shrinking them along the axes, while rotation matrices turn objects around a specified point or axis.
To use these matrices effectively, you first need to establish your coordinate system. Most transformations assume a standard Cartesian system, where each point is defined by its x and y (or z in 3D) coordinates. Once you have your points in this system, you can apply the appropriate transformation matrix. The beauty of matrix representation is that it allows you to combine multiple transformations into a single matrix. For instance, you can rotate and then translate an object by multiplying the rotation and translation matrices into a single composite matrix, which you then apply to all points. This approach simplifies complex moves and ensures consistency across the shape.
Understanding how transformation matrices operate within coordinate systems empowers you to manipulate figures with confidence. Whether you’re designing a graphic, modeling an object, or solving a geometry problem, knowing how to set up and apply these matrices streamlines your work. It also helps you visualize the effects of each transformation, making it easier to predict how shapes will change under various operations. By mastering the use of coordinate systems and transformation matrices, you’ll develop a solid foundation for exploring advanced geometric concepts and creating precise, controlled modifications in both two and three dimensions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Transformations Affect the Area of Geometric Figures?
Transformations can change the area of geometric figures through area scaling. When you perform a transformation like dilation, it impacts the area based on the scale factor squared. For example, if you double the size of a figure, its area increases by four times. Understanding the transformation impact helps you predict how a figure’s size and area will change, which is essential in geometry and real-world applications.
Can Transformations Be Combined Sequentially for Complex Shapes?
Isn’t it fascinating how the puzzle pieces of transformation sequences fit together like a perfect mosaic? Yes, you can combine transformations sequentially for complex shapes, creating composite operations. By doing so, you manipulate figures step-by-step, each transformation building on the last, allowing you to achieve intricate designs. This layered approach enhances your mastery, turning simple moves into powerful tools for exploring geometry’s endless possibilities.
What Is the Difference Between Rigid and Non-Rigid Transformations?
Rigid transformations preserve the shape and size of an object by maintaining coordinate preservation, meaning the distances and angles stay the same. Non-rigid transformations, however, cause shape distortion, altering the object’s proportions or structure. You can tell the difference by checking if the shape looks the same after the move—if it does, it’s rigid; if not, it’s non-rigid.
How Do Transformations Apply to Three-Dimensional Objects?
You can apply transformations to 3D objects by using 3D rotations to turn them around axes and perspective projection to display them realistically on 2D screens. These transformations help you manipulate objects in space, giving them depth and orientation. By understanding these techniques, you can create more dynamic models for animations, games, or simulations, making your 3D work more immersive and accurate.
Are There Real-World Applications of Geometric Transformations?
Yes, geometric transformations have real-world applications like coordinate mapping in GPS systems, where precise location data relies on these moves. They also help correct image distortion in photography and computer graphics, ensuring visuals look natural and accurate. By understanding how transformations work, you can manipulate images, maps, or models effectively, making them essential tools in fields like cartography, engineering, and digital imaging.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve mastered the methods of manipulating figures through translation, rotation, reflection, and dilation, you’re well on your way to becoming a geometry guru. Remember, practice perfects proficiency, so keep exploring and experimenting with transformations. With dedication and determination, you’ll develop a deeper understanding and a dynamic dexterity for geometric moves. Stay sharp, stay spirited, and continue to sharpen your skills—because in geometry, growth begins with a great grasp of the basics!