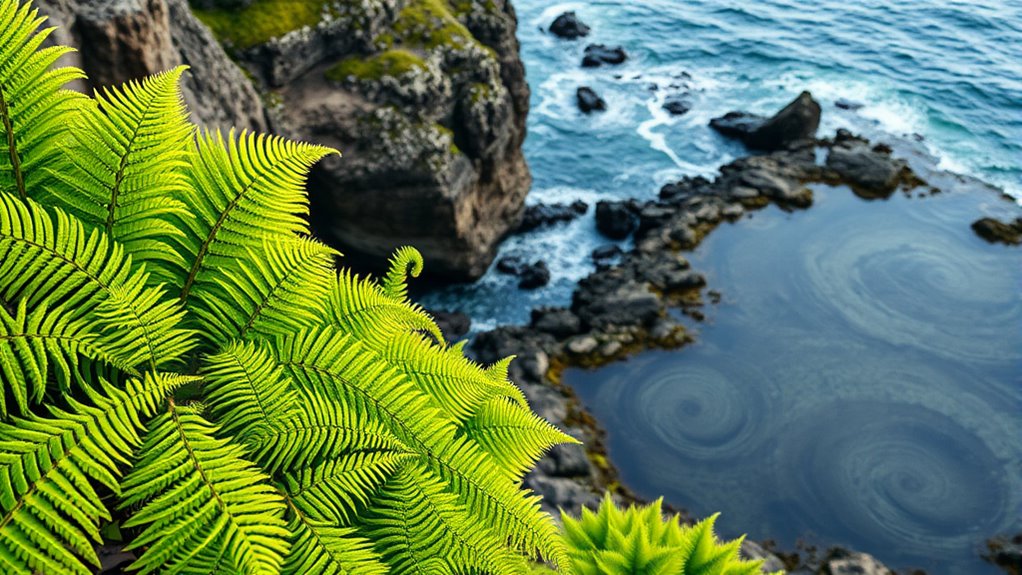
Fractals in nature show incredible self-similarity, meaning patterns repeat at different scales, from fern fronds to coastlines. You’ll notice these patterns in pinecones’ spirals, mountain ranges’ rugged edges, and galaxies’ swirling arms. These structures follow mathematical rules, creating efficient and resilient forms. Recognizing these patterns helps you see how nature’s beauty and complexity are connected by simple, universal principles. If you explore further, you’ll uncover even more fascinating examples of nature’s fractal design.
Key Takeaways
- Fractals are self-similar patterns found in natural forms like ferns, coastlines, and snowflakes.
- Fern fronds and Romanesco broccoli demonstrate recursive, miniature versions of their entire structure.
- Coastlines exhibit fractal complexity, with jagged edges repeating at different scales.
- Spiral patterns in shells and galaxies follow mathematical rules like Fibonacci sequences and fractal geometry.
- Recognizing fractals reveals the underlying order and efficiency in diverse natural systems.
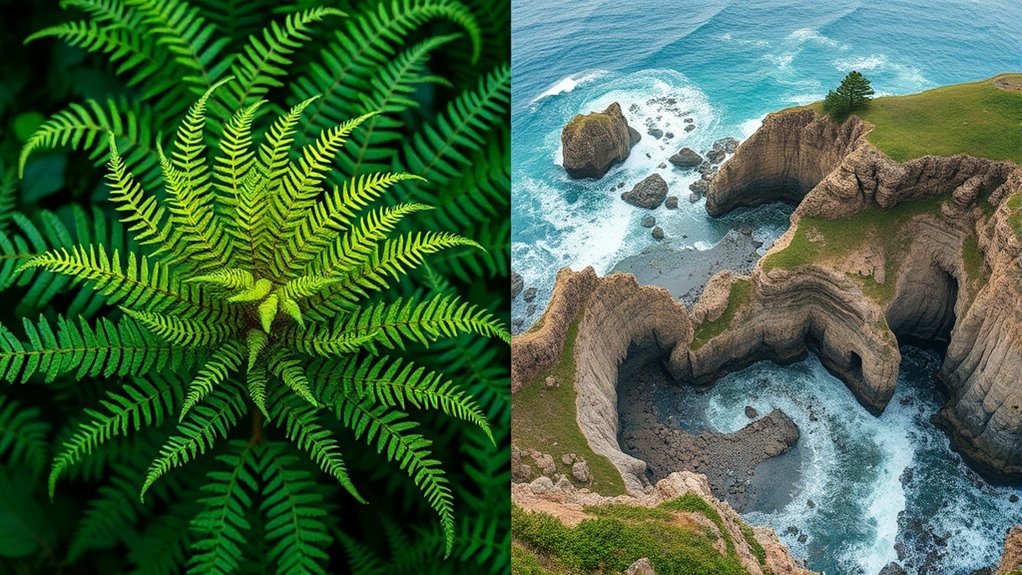

Have you ever noticed how certain patterns in nature mirror each other at different scales? This phenomenon, known as fractal geometry, reveals that many natural forms exhibit self-similarity, where small parts resemble the whole. When you observe fractal patterns in animals, you see structures that repeat across different levels of complexity. For instance, the branching of blood vessels and bronchial tubes mirrors the overall shape of the organism, allowing efficient delivery of nutrients and oxygen. Similarly, the intricate patterns on animal skins or the fractal-like arrangement of feathers display self-similar designs that serve functional and aesthetic purposes. These patterns aren’t random; they follow mathematical rules that optimize space, strength, and adaptability in the animal kingdom. The presence of supergranular patterns in various biological systems demonstrates how these fractal structures are integral to efficient biological functions. In plants, geometric self-similarity manifests vividly in structures like ferns, pinecones, and Romanesco broccoli. Fern fronds unfurl in a way that each smaller leaflet mimics the entire leaf’s shape, creating a repeating pattern across scales. This fractal arrangement maximizes light capture and space efficiency, which is essential for survival. Pinecones showcase spiral patterns that repeat at various levels, with each scale contributing to the cone’s overall structure. The spirals follow specific mathematical sequences, such as Fibonacci numbers, which help the plant pack seeds or scales in the most efficient way possible. Romanesco broccoli, with its stunning fractal geometry, illustrates how each floret is a miniature replica of the entire vegetable, highlighting how nature uses self-similarity to build complex, functional forms from simple rules. You can see that these fractal patterns aren’t just aesthetic; they’re rooted in the principles of efficiency and adaptability. By repeating shapes at different scales, nature creates structures that are both strong and lightweight, optimizing resource use. Whether it’s the branching of a tree, the pattern of a coastline, or the shape of a galaxy, fractals reveal a universal language of design that spans the cosmos. Recognizing these patterns in animals and plants helps you appreciate the underlying order in what might seem like chaos. They demonstrate how nature’s complexity arises from simple, repeating rules that work across scales, making the world more interconnected and beautiful than you might have realized at first glance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Fractals Influence Ecological Systems?
Fractals influence ecological systems by enabling self-similar growth patterns, which help organisms adapt efficiently to their environments. You’ll notice that these patterns optimize nutrient distribution, ensuring resources reach all parts of plants, animals, and ecosystems. This self-similar growth allows for better resilience and resource management, supporting the stability of ecological systems. Overall, fractals play a vital role in maintaining balance and functionality within nature’s complex networks.
Are All Natural Patterns Truly Fractal?
Think of natural patterns as a vast tapestry, but not all threads follow a perfect fractal design. Not every pattern is truly fractal; some are only approximations created through mathematical modeling or artistic representations. While many natural forms display fractal-like qualities, genuine fractals require infinite complexity and self-similarity. So, you’ll find some patterns that mimic fractals, but not all are inherently fractal in their structure.
Can Fractal Analysis Predict Environmental Changes?
Yes, fractal analysis can help predict environmental changes. By using fractal climate modeling, you can better understand complex weather patterns and identify shifts in climate trends. Additionally, analyzing fractal pollution patterns allows you to track how pollutants disperse over time, giving insights into potential health and ecological impacts. This approach enables more accurate forecasts and informed decision-making to address future environmental challenges effectively.
What Role Do Fractals Play in Animal Camouflage?
Like a master illusionist, fractals weave complexity into animal camouflage, making it harder for predators to spot their prey. You’ll find that many animals use fractal-like pattern complexity in their camouflage strategies, blending seamlessly into their environment. This recursive patterning mimics natural textures, enhancing concealment. Fractals deepen the illusion, creating a mesmerizing effect that disrupts predators’ vision, giving animals a crucial edge in survival.
How Are Fractals Applied in Environmental Conservation?
You can use fractals in environmental conservation by improving habitat modeling and pollution mapping. Fractal patterns help you analyze complex ecosystems, making it easier to identify vulnerable areas and monitor changes over time. By applying fractal mathematics, you gain detailed insights into natural landscapes and pollution spread, enabling more targeted conservation efforts. This approach allows you to safeguard ecosystems more effectively and ensure sustainable management of natural resources.
Conclusion
As you explore the world of fractals, you realize they’re like a secret language woven into nature’s tapestry. From the delicate fronds of ferns to jagged coastlines, these patterns echo endlessly, revealing nature’s hidden artistry. Just as a song repeats and evolves, fractals remind you that complexity is built from simple, repeating parts. Embrace this pattern, and you’ll see that nature’s beauty is a mesmerizing dance of fractal harmony, always revealing more to discover.