The P versus NP problem asks if every problem with solutions that can be verified quickly (NP) can also be solved quickly (P). If yes, many difficult problems become easy, impacting areas like cryptography and AI. If no, some problems are truly hard to solve efficiently. This question remains unsolved and is central to understanding what computers can achieve. Keep exploring to uncover more about this fascinating and important mystery.
Key Takeaways
- P consists of problems solvable quickly, while NP includes problems whose solutions can be verified quickly.
- The core question is whether every problem with quickly verifiable solutions can also be quickly solved.
- If P equals NP, many difficult problems become easy to solve, impacting fields like cryptography and AI.
- If P does not equal NP, some problems are inherently difficult to solve efficiently, shaping problem-solving approaches.
- The problem remains unsolved, with profound implications for computer science and the understanding of computational complexity.

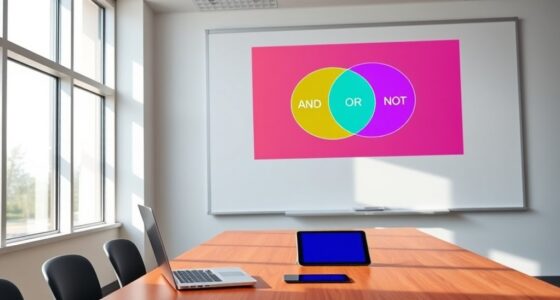
Have you ever wondered whether every problem whose solution can be quickly verified can also be solved quickly? This question cuts to the heart of one of the most famous unsolved problems in computer science: P versus NP. At its core, it’s about understanding the relationship between the difficulty of solving a problem and the difficulty of checking a solution. To get a grip on this, you need to consider algorithm complexity, which measures how the resources needed to solve a problem grow as the size of the input increases. Problems are categorized into classes based on their complexity, and this classification helps us understand which problems are efficiently solvable and which aren’t.
The P versus NP problem explores whether verifying solutions quickly implies solving problems quickly.
In simple terms, P is the class of problems that can be solved quickly—meaning there’s an algorithm that finds a solution in polynomial time. NP, on the other hand, is the class of problems for which, if someone gives you a solution, you can verify its correctness quickly, also in polynomial time. Think of it like this: solving the problem might be hard, but checking a proposed solution is easy. The big question: are these two classes the same? If they are, it means that every problem that can be verified quickly can also be solved quickly, which would have enormous implications across fields like cryptography, operations research, and artificial intelligence.
The problem’s difficulty lies in the fact that, for some problems, we don’t know whether efficient algorithms exist or not. The classification of problems into P and NP helps clarify this, but it doesn’t give the answer. Many problems are in NP but are believed to be outside of P, making them inherently difficult to solve efficiently. These are called NP-complete problems, and if you could find a polynomial-time solution for even one of them, you’d essentially prove that P equals NP. Conversely, proving that no such solution exists would show that P is not equal to NP. This is the essence of the P vs NP question—it’s about whether the ease of verification implies the ease of solving.
Additionally, research in computational complexity continues to explore the boundaries of these classes and their implications for practical problem-solving. Until someone solves it, you’re left with a compelling mystery that influences how algorithms are designed and how problems are approached in computing. The classification of problems based on their algorithm complexity helps set expectations for what can be achieved efficiently. If P were to equal NP, many tasks currently considered hard would suddenly become easy, transforming entire industries. But if P is different from NP, it confirms that some problems will always be challenging, guiding researchers to develop approximate or heuristic solutions instead of exact ones. The P vs NP problem remains a fundamental question, shaping the way you think about the limits of computation and problem-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does P Vs NP Impact Everyday Technology?
You rely on algorithms daily, and if P equals NP, it could revolutionize your experience by making complex problem-solving much faster. This impacts computational complexity, potentially allowing computers to efficiently solve tasks like encryption, logistics, and data analysis. Conversely, if P doesn’t equal NP, many problems remain hard, meaning your devices might struggle with optimization and security, keeping certain tech limitations in place.
What Are Practical Examples of P Problems?
You encounter practical P problems daily, like sorting emails or finding the shortest route on a map. These problems have efficient algorithms, making them easy to solve quickly. You can classify these problems as having polynomial-time algorithms, meaning they’re efficiently solvable. Recognizing problem classification helps you understand which tasks can be automated and optimized, ensuring algorithm efficiency in everyday applications.
Has Anyone Claimed to Prove P Vs NP?
Think of the P vs NP problem like a mountain climber trying to reach the summit. Many researcher claims and proof attempts exist, but none have been universally accepted as definitive. You should know that no one has convincingly proved whether P equals NP or not. The mathematical community remains cautious, as the problem’s solution would revolutionize computer science, yet it still stands as an open challenge for the brightest minds.
What Are the Consequences if P Equals NP?
If P equals NP, cryptography security could collapse because many encryption methods rely on problems being hard to solve quickly. You might see faster algorithm design, solving complex problems efficiently, but it could also mean that previously secure systems become vulnerable. This would drastically change computer security and problem-solving, forcing you to rethink how algorithms are built and how data remains protected in digital environments.
Are There Ongoing Efforts to Solve P Vs NP?
Like chasing a mirage, ongoing efforts to solve P vs NP continue to push boundaries in computational complexity and algorithm development. Researchers worldwide work tirelessly, exploring new theories and approaches, hoping to crack the code. While no definitive solution exists yet, these persistent endeavors fuel progress in understanding problem-solving limits, reminding you that persistence and curiosity are essential in unraveling even the toughest mathematical mysteries.
Conclusion
So, here’s the thing: about 1 in 10 computational problems are classified as NP-hard, meaning they’re incredibly tough to solve quickly. If P equals NP, it would revolutionize fields like cryptography and data analysis overnight. Right now, scientists have been working on this puzzle for over 50 years. It’s a mind-boggling challenge, but understanding it could open impossible solutions and reshape our digital world forever.