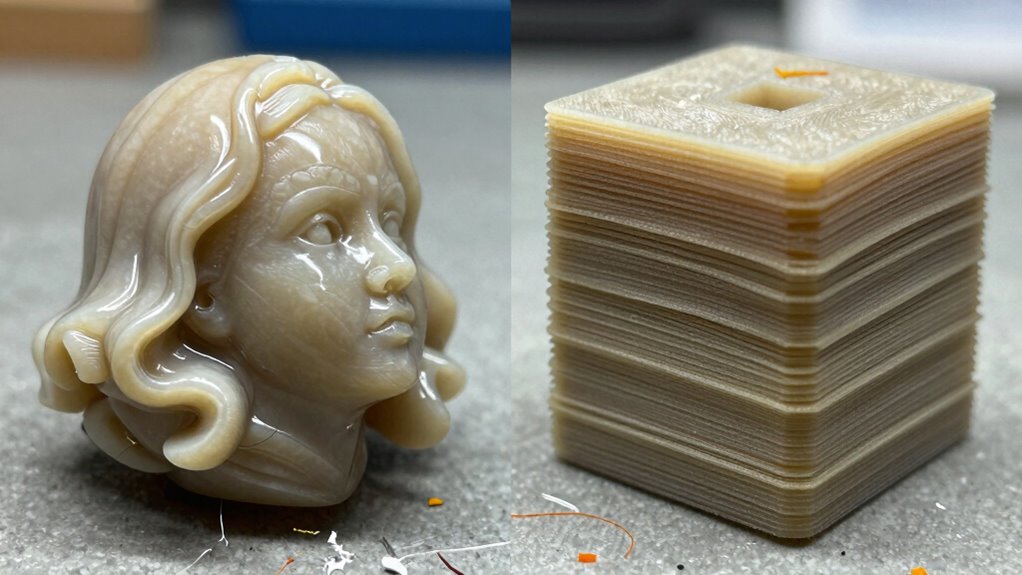
If you’re comparing FDM and resin printing, you’ll find FDM is better for larger, durable parts with rougher surfaces, while resin excels at detailed, smooth finishes but is more brittle. FDM is easier to handle and safer overall, but resin involves chemicals and post-processing. Both have their strengths and mess factors. Keep exploring to understand which method fits your projects and preferences best.
Key Takeaways
- Resin printing offers superior detail and smooth surfaces, ideal for miniatures and intricate models, compared to FDM’s visible layer lines.
- FDM parts are generally more durable and impact-resistant, while resin prints tend to be more brittle and prone to cracking.
- Resin printing involves handling toxic chemicals, requiring careful post-processing and proper ventilation; FDM is cleaner and safer with filament.
- FDM is faster and more cost-effective for large, functional objects, whereas resin excels in high-resolution, small, detailed projects.
- Resin printing produces messier workflows due to resin handling and curing, while FDM involves straightforward filament extrusion with less cleanup.
How Do FDM and Resin 3D Printing Work?
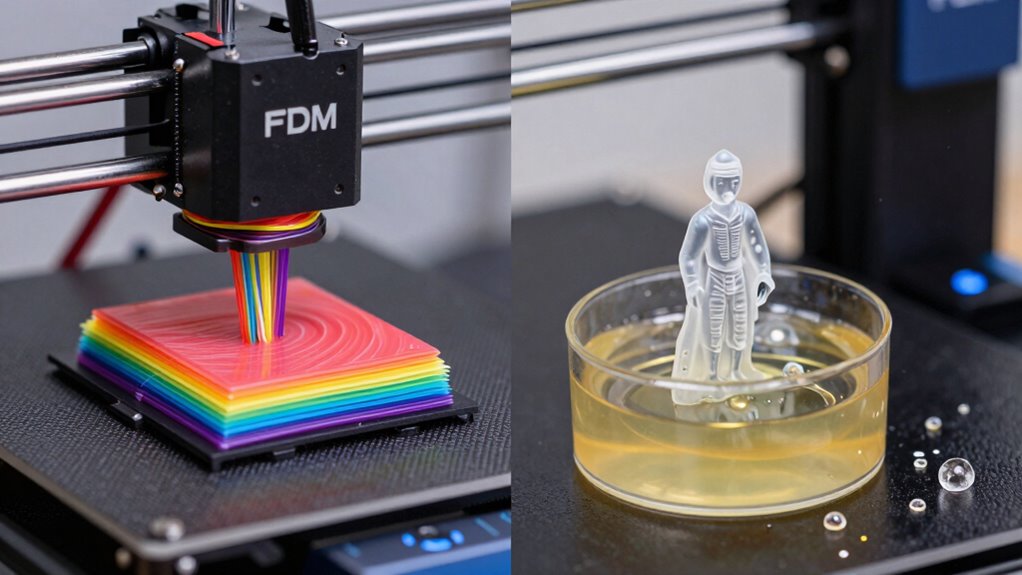

While both FDM and resin 3D printing create objects layer by layer, they do so through different processes. With FDM, you melt filament and extrude it through a nozzle, building your model from the bottom up. Support structures are often needed to stabilize overhangs, and color options depend on filament choices, offering a range of hues. Resin printing, on the other hand, uses a liquid resin that’s cured by a light source, layer by layer. It generally produces finer details and smoother surfaces. Support structures are essential for complex geometries but can be more delicate to remove. Unlike FDM, resin printers typically offer fewer color options, as resins are usually available in limited shades. Both methods have unique workflows, advantages, and limitations based on their processes. Additionally, the precision and detail achieved by resin printing make it especially suitable for intricate designs and prototypes. Furthermore, advancements in European cloud innovation are supporting the development of more sophisticated 3D printing technologies, enhancing their capabilities and accessibility.
What Are the Main Differences Between FDM and Resin Printing?
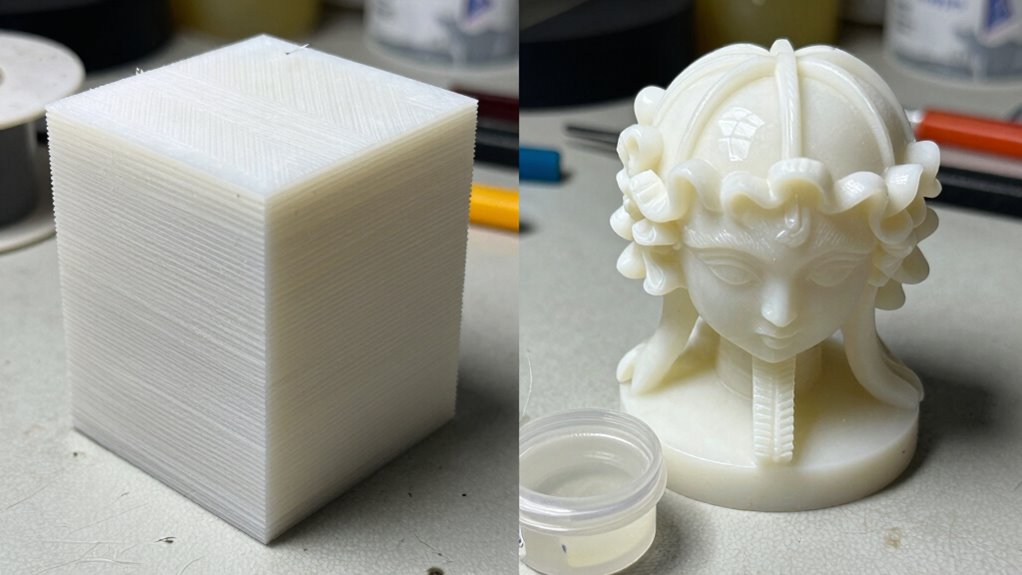

FDM and resin printers use different technologies, which affect how they build models and the materials they use. You’ll notice distinct differences in the properties of their printed objects, like strength and flexibility. Additionally, their finish and level of detail vary, impacting the quality and complexity of your projects.
Printing Technology Differences
Understanding the main differences between FDM and resin printing involves examining how each technology builds objects. FDM uses filament extrusion, where heated filament is melted and layered to create models. Resin printing, on the other hand, relies on resin curing with light, solidifying small layers of liquid resin. This fundamental contrast impacts speed, detail, and complexity. FDM typically produces durable parts, but with rougher surfaces. Resin printers excel in fine detail and smooth finishes but require careful handling. The table below highlights these emotional differences:
| Aspect | FDM | Resin Printing | Emotional Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build Process | Filament extrusion | Resin curing with light | Creativity vs. Precision |
| Surface Finish | Slightly rough | Ultra-smooth | Satisfaction vs. Frustration |
| Speed | Faster for larger objects | Slower, detailed prints | Efficiency vs. Detail |
| Material Handling | Filaments, easy to store | Liquid resin, messy and delicate | Convenience vs. Mess |
| Detail Level | Moderate | Extremely high | Pride in detail vs. Overwhelm |
Additionally, advancements in Free Floating technology are continuously influencing how these printers operate and their overall user experience.
Material Properties Contrast
The material properties of FDM and resin printing markedly influence their applications and handling. FDM filaments typically offer greater material flexibility, making parts more resilient and less prone to cracking under stress. In contrast, resin prints tend to be more rigid, providing higher detail but less flexibility. Chemical stability also varies: FDM materials generally withstand environmental factors better, with many filaments being more resistant to moisture and heat. Resin materials, however, can be more sensitive to chemicals and UV exposure, which may degrade their properties over time. Additionally, essential oils can sometimes be used to clean or maintain certain printers, especially when dealing with resin residues. It’s important to understand the material properties that influence print durability and post-processing requirements. Recognizing the material differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate printing method for specific project needs—whether you require durable, flexible parts or highly detailed, rigid ones. Moreover, understanding the material compatibility with various post-processing techniques ensures optimal results and longevity of your prints. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right printing method based on your project needs—whether you require durable, flexible parts or highly detailed, rigid ones.
Finish and Detail Variations
Material properties profoundly influence the finish and level of detail achievable with each printing method. With FDM printing, the layer finish often shows visible lines, and details may lack sharpness, especially on complex surfaces. The layer height impacts the smoothness, but fine details can be challenging to replicate accurately. Resin printing, however, produces a much smoother layer finish and exceptional detail clarity. The resin’s high resolution allows for intricate features and sharp edges, making it ideal for detailed miniatures or prototypes. You’ll notice that resin prints typically require less post-processing to achieve a polished look. In contrast, FDM’s finish may need sanding or smoothing, but it’s better suited for larger, less detailed objects. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right method for your project’s desired finish and detail.
Is FDM or Resin Better for Surface Finish and Detail?
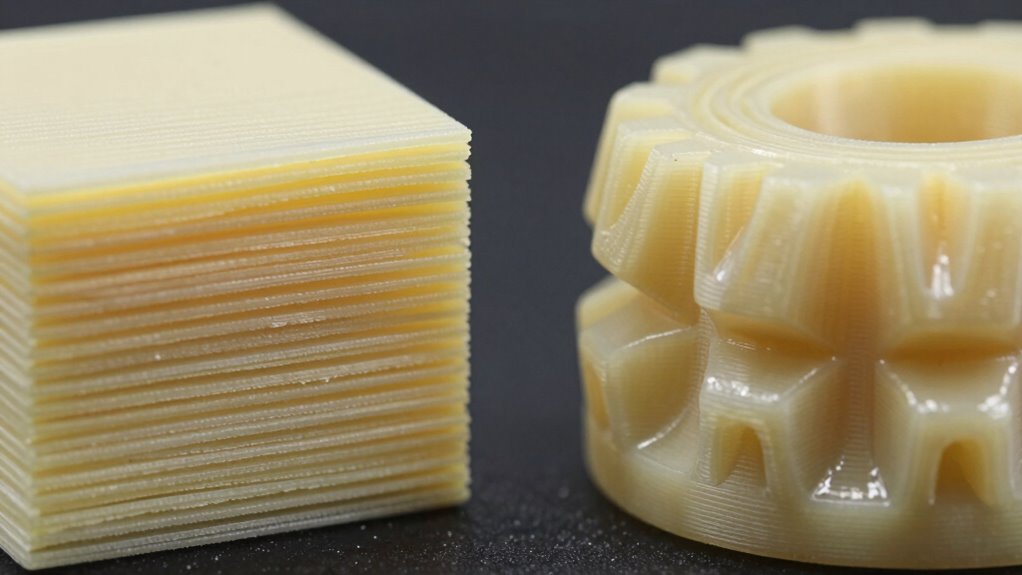
When it comes to surface finish and detail, resin printers generally outperform FDM models thanks to their high-resolution capabilities. Resin printing produces smoother surfaces and finer details, making it ideal for intricate models and miniatures. FDM printers often leave layer lines and rougher surfaces, which can be smoothed but rarely match resin’s level of finesse. The table below highlights key differences:
| Feature | Resin Printing | FDM Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Very smooth, minimal post-processing | Slightly rough, requires smoothing |
| Fine Detail | Excellent, high-resolution details | Good but limited by layer height |
| Layer Lines | Nearly invisible | Visible |
| Complexity of Features | Captures fine features well | Struggles with tiny details |
| Post-Processing | Usually needed for best finish | Less intensive |
Which Prints Are Stronger and More Durable: FDM or Resin?

When comparing strength and durability, you’ll notice that FDM and resin prints differ markedly. FDM parts generally have better impact resistance and layer adhesion, making them more durable for functional uses. Resin prints, however, tend to be more brittle, which affects their ability to withstand stress over time. Additionally, support breakfast options such as high-protein meals can contribute to overall energy and focus during long printing sessions. Ensuring proper material selection can also influence the final strength and longevity of your prints, aligning with your specific project needs. Considering print orientation during setup can further improve the strength characteristics of your finished piece. Exploring layer height settings can also impact the overall strength and surface quality of your prints. Incorporating quality assurance practices helps identify potential issues early, ensuring consistent and reliable results in your printing projects.
Material Strength Differences
FDM and resin prints differ markedly in their strength and durability, with each technology excelling in different areas. FDM prints tend to have stronger layer bonding, which helps resist breaking along layer lines, making them more durable under stress. However, the filament materials used in FDM, like PLA or ABS, can be more brittle, especially if not printed with ideal settings. Resin prints, on the other hand, usually feature excellent detail and a smoother surface but are more prone to material brittleness. This brittleness means resin parts can crack or shatter more easily under impact or stress. While FDM parts generally withstand rough handling better, resin prints excel in precision but may require careful handling to avoid damage. Material properties also play a crucial role in determining the overall strength and suitability of each type for different applications. Additionally, understanding the mechanical characteristics of each material can help optimize print settings for better performance. For instance, layer adhesion significantly influences the overall robustness of FDM parts, making them more resistant to delamination.
Layer Adhesion Quality
Layer adhesion quality plays a crucial role in determining the overall strength and durability of 3D prints. FDM and resin prints differ markedly in how well their layers bond. FDM relies on melting filament and cooling, which can lead to adhesion inconsistencies if temperatures fluctuate. Resin printing, however, creates a chemical bond between layers, resulting in superior layer bonding. This means resin prints typically have better adhesion consistency, making them more resistant to delamination.
| Aspect | FDM | Resin | Impact on Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer bonding | Melting filament, cooling process | Chemical curing, layer-to-layer bond | Generally weaker than resin |
| Adhesion consistency | Variable, affected by temperature | Consistent, due to chemical bonds | Resin offers more uniform adhesion |
| Impact on durability | Slightly lower due to layer gaps | Higher, stronger layer bonding | Resin prints tend to be more durable |
Impact Resistance Levels
Although both FDM and resin prints have their strengths, their impact resistance differs markedly. FDM prints generally offer higher impact durability, making them better suited for objects that need to withstand force and rough handling. Their layer-by-layer construction creates a more resilient structure, providing better force resilience against impacts. Material properties play a crucial role in determining overall durability and impact resistance. Resin prints, on the other hand, tend to be more brittle and may crack or shatter under sudden force. While they excel in detail and surface finish, their lower impact resistance makes them less ideal for applications requiring durability against impact. Understanding material properties is crucial when selecting the appropriate 3D printing method for your project. Additionally, the choice of filament or resin material can significantly influence the impact resistance of your print, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right print materials for your specific needs. Proper print settings can also enhance the impact resistance of your finished piece, especially in FDM printing. Moreover, selecting appropriate printing parameters can improve the overall toughness and resilience of the final product.
What Safety Precautions Should You Know for FDM and Resin Printing?

Safety should always be a top priority when working with 3D printers, as both FDM and resin printing involve potentially hazardous materials and processes. Resin hazards include skin irritation, inhalation of fumes, and chemical exposure, so wearing gloves and eye protection is essential. Proper ventilation needs are critical with resin printing to disperse harmful fumes and prevent buildup in your workspace. For FDM printing, ensure good airflow to avoid inhaling filament fumes and dust. Keep your workspace clean and handle materials carefully to minimize risks. Never leave printers unattended during operation, and always follow manufacturer safety guidelines. Regularly inspect your equipment for leaks or wear, and store chemicals safely out of reach. Staying vigilant helps protect your health and keeps your printing environment safe. Additionally, understanding the sound vibrations involved in sound healing science can inform safer practices when integrating auditory therapies into your workspace. Moreover, familiarizing yourself with ventilation requirements can significantly reduce the buildup of potentially harmful fumes during resin printing. Proper personal protective equipment is also essential to prevent direct contact with hazardous substances during handling and maintenance. Being aware of material-specific safety protocols ensures comprehensive protection during all stages of the printing process. Incorporating routine safety checks can further help identify potential hazards early and maintain a safe working environment.
How Much Do FDM and Resin 3D Printers Cost?

The cost of FDM and resin 3D printers varies considerably, depending on their features and intended use. For a basic FDM printer, expect to spend between $200 and $500, making it budget-friendly for hobbyists. Mid-range models range from $500 to $1,500, offering better build quality and features. High-end FDM printers can exceed $2,000 if you need industrial-grade capabilities. Resin printers, on the other hand, start around $300 for entry-level units but often cost $1,000 to $3,000 for more precise, professional models. When considering the cost comparison, keep in mind your budget considerations, as resin printers tend to have higher ongoing resin costs and maintenance expenses. Balancing initial investment with long-term use helps determine the best choice for your needs.
Are FDM or Resin Printers Easier for Beginners to Use?

Choosing between FDM and resin printers depends on your experience level, but generally, FDM printers are easier for beginners to operate. With FDM, you mainly handle filament selection and simple setup, making it straightforward to start. Resin printers, on the other hand, involve more post processing challenges, such as cleaning and curing delicate prints. You’ll also need to learn how to handle resin safely and precisely. Visualize:
- Loading filament smoothly into the extruder without jams
- Managing filament spool tension for consistent prints
- Carefully removing prints from the build plate without breakage
FDM printers tend to have less complex maintenance and fewer steps in post processing, making them ideal for those new to 3D printing. Resin printers require more patience and attention to detail, which can be intimidating for beginners. Additionally, understanding the post-processing steps involved in resin printing is essential for achieving high-quality results.
What Are the Best Projects for FDM and Resin Printing?
Wondering which projects suit FDM or resin printers best? FDM printers excel at larger, functional items like prototypes, tool holders, and household upgrades because they handle bigger builds easily. Resin printers shine with detailed miniatures, jewelry, and intricate models thanks to their fine resolution. When working with resin, focus on proper post processing tips, such as thorough cleaning and curing, to achieve the best results. For FDM prints, good filament storage helps prevent warping and maintains print quality. Consider your project’s needs: if you want durability and size, go FDM; if you need fine detail and smooth surfaces, resin is ideal. Both require attention to post processing and storage to ensure your prints look professional and last longer.
How Do Speed and Efficiency Compare Between FDM and Resin?

When comparing speed and efficiency, it’s important to recognize how each printing method fits different project timelines. FDM generally offers faster turnaround for larger, less detailed parts, while resin printing excels in producing small, intricate models quickly. Resin printers can reduce post processing challenges with fewer finishing steps but require careful resin handling. FDM needs filament storage requirements to prevent moisture absorption, which can slow down production. Resin printing often involves longer setup times due to resin curing and cleaning, but overall, it produces high-detail parts faster. Consider your project’s complexity and desired finish—resin may be more efficient for detailed miniatures, while FDM suits larger prototypes with less detail. Balancing speed with ease of post processing and storage impacts your overall efficiency.
Which 3D Printing Method Is Right for Your Needs?

Choosing the right 3D printing method depends on your material options and the complexity of your designs. FDM printers work well with a wide range of filaments and larger, simpler parts, while resin printers excel at detailed, intricate models with specific resin types. Consider your project’s material needs and complexity to determine which method best fits your goals.
Material Compatibility
Understanding which 3D printing method suits your project depends heavily on material compatibility. FDM printers can handle a wide variety of thermoplastics, offering extensive color options and the ability to customize filaments. They’re also more environmentally friendly, with better recycling potential for used filament spools and scraps. Resin printers, on the other hand, work with specialized liquid resins that produce detailed, high-quality finishes but are limited in color choices and less recyclable. Consider these factors:
- Wide range of filament colors for vibrant, customizable prints
- Limited resin color options, often requiring post-processing for color changes
- Better recycling potential with filament spools compared to liquid resins
Matching your material needs to your chosen method guarantees ideal results and project flexibility.
Print Complexity
The complexity of your print design plays a crucial role in selecting the right 3D printing method. If your design has high intricacy or detailed features, resin printing often handles this better due to its superior resolution. Resin printers excel at capturing fine detail and complex geometries, making them ideal for intricate models, jewelry, or detailed prototypes. In contrast, FDM printers are more suitable for simpler, less detailed designs, especially when durability and larger build sizes are priorities. While FDM can struggle with very fine features, resin printing can produce smooth, highly detailed results with ease. Consider your design’s complexity carefully—if you need precision and intricate detail, resin is the way to go; for larger, straightforward prints, FDM works well.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Post-Processing Differ Between FDM and Resin Prints?
Post-processing for FDM and resin prints differs mainly in support surface preparation and curing process. With FDM, you remove supports and sand surfaces, often needing to clean with alcohol. Resin prints require careful support removal and a thorough curing process under UV light to solidify the material. Resin post-processing is more delicate, while FDM is simpler but may need more sanding and finishing to achieve smoothness.
What Environmental Impacts Are Associated With Each Printing Method?
You should consider that FDM printing generally has a lower environmental impact because it produces less material waste and uses recyclable filament options. Resin printing, on the other hand, involves hazardous chemicals and generates more waste, which can be difficult to dispose of safely. Both methods consume energy, but resin’s chemical waste poses a higher environmental concern. Being mindful of waste and chemical disposal helps reduce your printing footprint.
Can FDM and Resin Printers Be Combined for Complex Projects?
Think of combining FDM and resin printers as orchestrating a symphony of hybrid fabrication, where your project becomes a masterpiece of multi-material integration. Yes, you can merge these technologies for complex projects, leveraging FDM’s strength and resin’s fine detail. This fusion allows you to craft intricate, durable parts with precision, opening new creative horizons. With careful planning, your designs can seamlessly blend the best of both worlds into one cohesive creation.
How Do Filament and Resin Material Options Vary?
You’ll find that filament varieties include PLA, ABS, PETG, and flexible options, each offering different strength, flexibility, and ease of use. Resin types vary as well, such as standard, tough, flexible, and castable resins, catering to different project needs. Depending on your goals, selecting the right filament or resin type lets you optimize for detail, durability, or flexibility, ensuring your prints meet your specific requirements.
What Maintenance Is Required for FDM Versus Resin Printers?
Like a vigilant guardian, you must regularly clean and calibrate your printers. For FDM, store filament properly to prevent moisture damage and check for nozzle clogs. Resin printers require careful resin disposal, ensuring you don’t spill or waste material, and cleaning the resin vat and print bed afterward. Both demand routine maintenance to keep prints pristine, but resin printers need extra attention to resin handling and disposal, much like tending a delicate garden.
Conclusion
Choosing between FDM and resin printing is like selecting the perfect paintbrush for your artwork—you’ll want the one that brings your vision to life. FDM offers durability and affordability, great for larger, practical projects. Resin printing delivers incredible detail and smooth finishes, ideal for miniature or intricate designs. Consider your needs, safety, and experience to pick the right tool. Whichever you choose, you’re about to open a world of creative possibilities waiting to be shaped.









