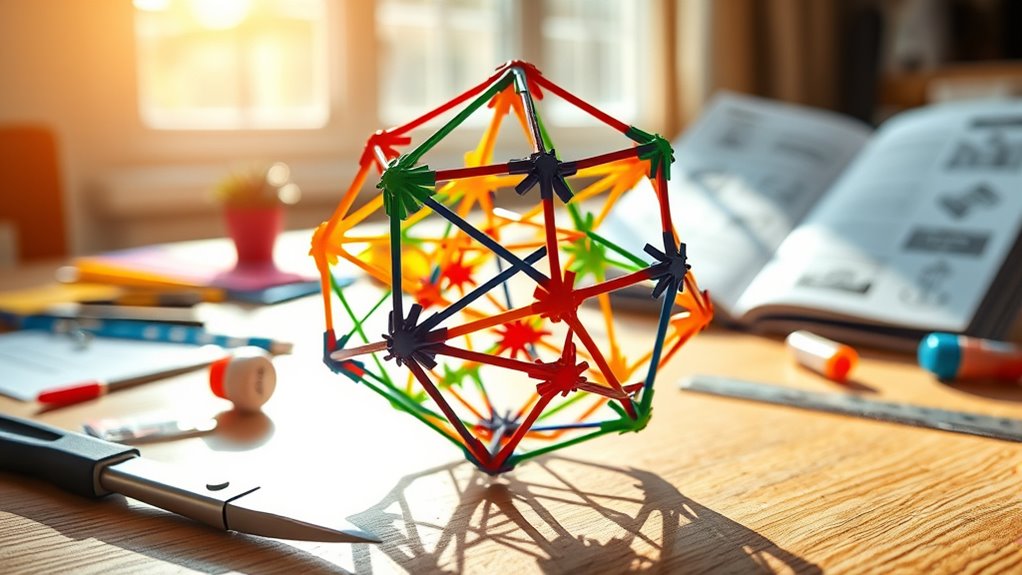
To build your own polyhedron model at home, start by choosing a shape like a cube, tetrahedron, or dodecahedron. Use sturdy paper or thin cardboard, and craft precise nets with a ruler and protractor. Carefully cut, fold, and glue along the edges, paying close attention to angles and symmetry. This hands-on project lets you explore geometric principles firsthand, and if you keep exploring, you’ll discover even more about these fascinating 3D shapes.
Key Takeaways
- Gather materials like sturdy paper, scissors, ruler, protractor, and glue for accurate construction.
- Draw and cut out the polyhedron net, ensuring correct measurements and angles based on geometric principles.
- Fold along edges precisely, forming the shape while maintaining symmetry and proper alignment.
- Secure tabs with glue, paying attention to angles to preserve the model’s structural integrity.
- Reflect on geometric relationships during assembly to deepen understanding of polyhedron properties and aesthetics.
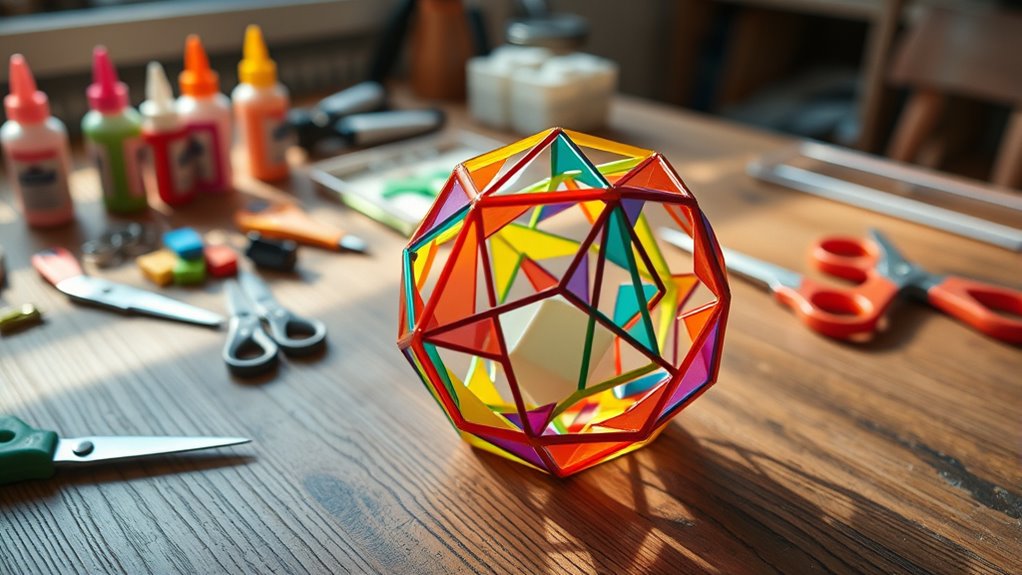

Creating your own polyhedron model is a rewarding and educational project that combines craftsmanship with geometric understanding. As you set out on this journey, you’ll discover that building a polyhedron isn’t just about assembling shapes; it’s about engaging with the fundamentals of geometric constructions and exploring the rich history of polyhedra. The study of polyhedra dates back thousands of years, with ancient civilizations creating models to understand the structure of the universe and the nature of symmetry. Familiarizing yourself with this polyhedron history can deepen your appreciation for the shapes you’re about to craft. It reveals how mathematicians and artists alike have appreciated these forms for their aesthetic and structural qualities. By constructing a model, you’re engaging in a tradition that spans cultures and centuries.
Crafting polyhedron models connects craftsmanship, geometry, and centuries of mathematical and artistic tradition.
To start, gather your materials: sturdy paper or thin cardboard, scissors, ruler, protractor, glue, and possibly a compass. Your goal is to create geometric constructions that will serve as the foundation for your polyhedron. You’ll begin by drawing precise nets — flat patterns that fold into the three-dimensional shape. These nets are based on the properties of the particular polyhedron you want to build, such as a tetrahedron, cube, or dodecahedron. Using your ruler and protractor, carefully measure and draw the edges and angles, following the principles of geometric constructions. For example, constructing a regular tetrahedron requires equilateral triangles, so you’ll need accurate measurements to guarantee symmetry. As you work through these constructions, you’ll notice how each shape relies on specific angles and proportions, reinforcing your understanding of geometric relationships. Engaging with geometric constructions can deepen your grasp of the underlying principles that make these shapes so fascinating.
Once you’ve completed your net, cut it out with scissors and fold along the edges. Use glue to secure the tabs and assemble the three-dimensional form. Pay close attention to the angles and joints — precise folding ensures your model holds its shape. As you assemble, reflect on how the geometric constructions you’ve executed relate to the polyhedron’s properties. This hands-on process helps solidify your understanding of the polyhedron’s structure and symmetry, connecting theory to tangible form. Throughout this process, you’re not only creating a model but also engaging with the mathematical principles that govern these shapes. This activity also offers a glimpse into the history of polyhedra, revealing how ancient artisans and mathematicians visualized complex forms long before modern technology.
Building your own polyhedron model at home is more than a craft project; it’s an exploration of geometry and history. By mastering geometric constructions and assembling your shape, you gain insight into the timeless beauty and mathematical significance of polyhedra. It’s a fulfilling hands-on experience that brings abstract concepts into reality, showcasing the elegance of symmetry and shape that have fascinated humans for centuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Tools Are Necessary for Building the Model?
To build your polyhedron model, you’ll need basic tools like scissors, glue, and a craft knife. Focus on good material selection—choose sturdy paper or cardboard for durability. Keep your tools well-maintained to guarantee clean cuts and precise assembly. Always handle your tools carefully, and store them properly after use. This way, you’ll enjoy a smooth building process and create a high-quality model that lasts.
How Long Does It Typically Take to Complete?
You probably wonder about the time estimation for building a polyhedron model. Generally, it takes about 1 to 3 hours, depending on your skill level. Beginners might need more time to carefully cut and assemble each piece, while experienced crafters can finish faster. Your pace and familiarity with the tools impact the total time. So, plan accordingly and enjoy the process of creating your geometric masterpiece!
Can This Project Be Scaled for Larger Models?
You can definitely scale this project up, but it’s not a walk in the park. Scaling techniques become essential, and you’ll need to take material considerations into account carefully. Larger models demand sturdier materials and precise measurements to keep everything aligned. While it’s doable, be prepared to put in extra planning and patience. With the right adjustments, you can create impressive, bigger polyhedron models that truly stand out.
Are There Safety Precautions to Consider?
When working on your polyhedron model, safety precautions are essential. Always wear appropriate safety gear like goggles and gloves to protect yourself from sharp edges or tools. Verify your workspace is well-ventilated, organized, and free of hazards to promote workspace safety. Keep tools properly maintained and follow instructions carefully. Taking these steps minimizes risks, keeps you safe, and makes your modeling experience enjoyable and accident-free.
Where Can I Find Additional Design Templates?
If you’re looking for additional design templates, start by exploring online template sources like educational websites, 3D modeling platforms, and design communities. These platforms offer a variety of templates that can spark your creativity and improve your polyhedron models. You can also browse through design inspiration sites or forums where hobbyists share their projects. This way, you’ll find new ideas and customize your models to fit your style and skill level.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve built your own polyhedron model, you might wonder if these shapes hold secret mathematical truths. Some believe polyhedra reveal hidden patterns in nature and the universe, from crystal structures to cosmic formations. While this theory is fascinating, it’s still debated among scientists. But one thing’s certain—you’ve taken a step toward understanding these geometric wonders firsthand. Keep exploring, and who knows? Maybe you’ll uncover new mysteries hiding in plain sight.