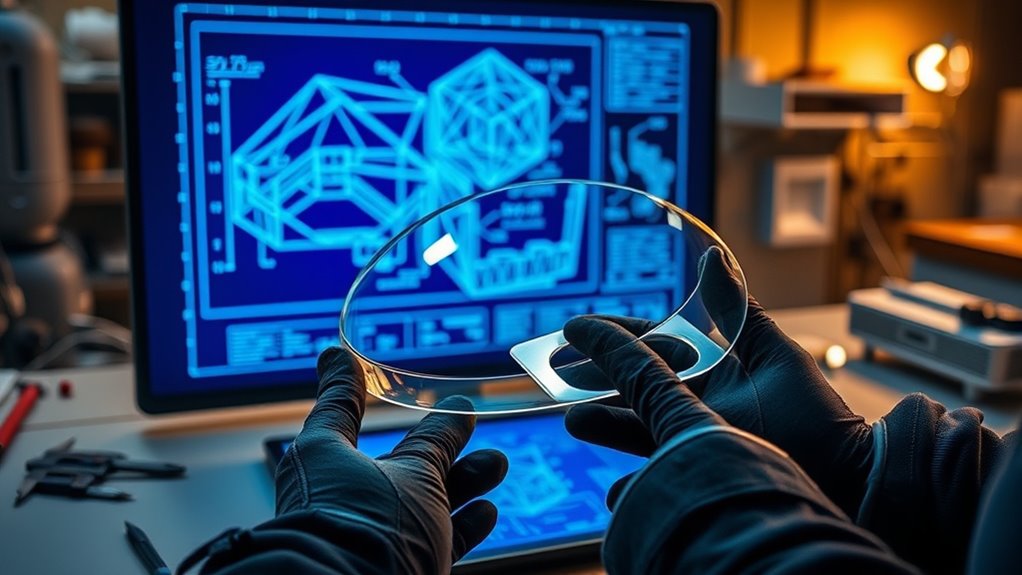
In manufacturing, geometry plays a critical role in turning CAD blueprints into real parts. You use precise geometric dimensioning to specify shapes, sizes, and relationships, minimizing errors during production. Material tolerances allow for practical variation, balancing quality and cost. Ensuring parts meet these standards through quality control guarantees that finished products align with original designs. Continuing will reveal how mastering these principles helps you produce high-quality, reliable components efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- Geometric dimensioning clearly defines feature size, shape, and orientation to ensure precise manufacturing and reduce errors.
- Material tolerances specify allowable deviations, balancing cost, quality, and functionality during production.
- CAD designs incorporate geometric standards that guide manufacturing processes and enable accurate translation into physical parts.
- Quality control uses measurement tools to verify components meet specified geometric and material tolerances.
- Managing manufacturing variations through tolerances maintains product integrity and ensures reliable assembly and performance.
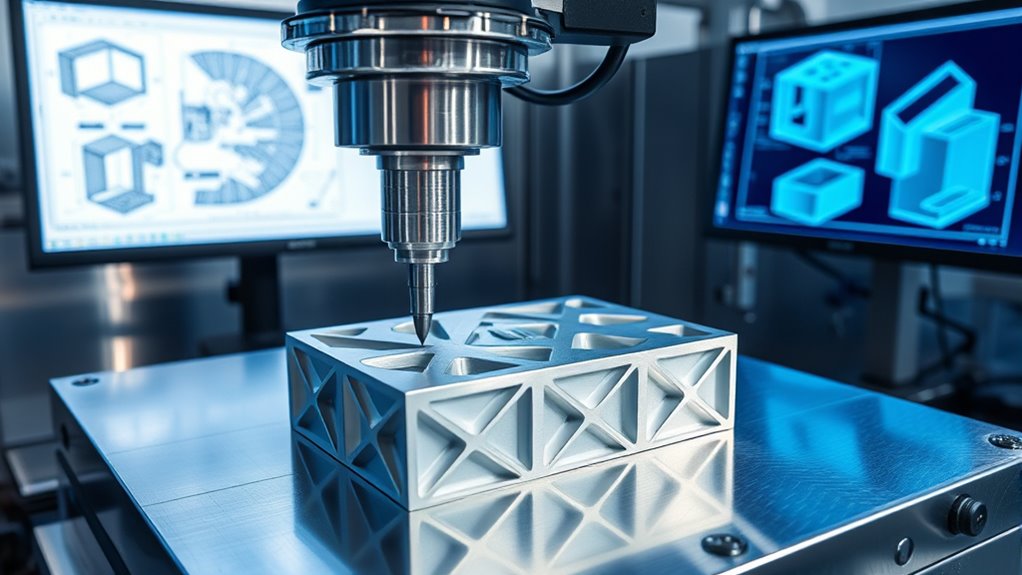

Have you ever wondered how precise parts and products come to life in manufacturing? It all begins with understanding how to translate complex designs into tangible objects. This process relies heavily on the use of geometric dimensioning and material tolerances to guarantee every component fits perfectly and functions as intended. Geometric dimensioning provides a clear language for defining the exact shape, size, and orientation of each feature on a part, minimizing ambiguity and errors during production. By specifying the relationships between different features, it ensures that every component maintains the intended geometry, even when manufacturing variations occur. Material tolerances, on the other hand, set permissible limits for deviations in dimensions and material properties, giving you a clear framework for how much variation is acceptable without compromising performance or safety. Together, these concepts form the backbone of precision engineering, guiding everything from initial CAD blueprints to the final inspection of finished products.
When you start designing a part in CAD, you’re working within a set of geometric dimensioning standards that define how measurements and relationships are communicated. These standards help guarantee that everyone involved in the manufacturing process understands the exact specifications, reducing the risk of misinterpretation. As the design moves from a digital blueprint to physical production, material tolerances become crucial. They allow for slight variations in manufacturing processes—like machining, casting, or 3D printing—while still maintaining the integrity of the part. If tolerances are too tight, production costs increase, and the risk of rejection rises. If they’re too loose, parts may not fit or function properly, leading to potential failures or safety issues. Striking the right balance involves carefully analyzing the design requirements and manufacturing capabilities.
Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control plays a vital role in guaranteeing these tolerances are met. Using precise measurement tools, inspectors verify that parts adhere to the specified tolerances and geometric constraints. This step is essential to prevent defects and guarantee consistency across production batches. By adhering to strict geometric dimensioning and material tolerances, you guarantee that each part produced aligns with the original design intent. This guarantees reliability, functionality, and safety in the final product. Additionally, understanding how to manage manufacturing variations ensures that the final product remains within acceptable limits despite inherent process deviations. Ultimately, understanding and applying these principles allows you to turn detailed CAD drawings into high-quality, precisely manufactured items that meet rigorous standards, enabling complex assemblies to work seamlessly in real-world applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Geometry Influence Material Selection in Manufacturing?
Geometry influences your material selection because it determines the material properties required to withstand specific shapes, sizes, and tolerances. Precise geometric designs demand materials with suitable strength, flexibility, or thermal properties. If your design requires high geometric precision, you need materials that can maintain tight tolerances without deforming. Choosing the right material guarantees your manufacturing process produces parts that meet specifications and perform reliably in their intended application.
What Role Does Geometry Play in Quality Control Processes?
You might think quality control is all about inspection, but it’s really about catching those subtle geometric defects that can hide in plain sight. Precision measurement becomes your best friend, ensuring every part matches its blueprint. When you overlook geometry’s role, small errors slip through, risking product failure. Ironically, perfect geometry isn’t just about looks—it’s the backbone of consistent quality, saving you time and money in the long run.
How Are Geometric Tolerances Integrated Into CAD Designs?
You integrate geometric tolerances into CAD designs by specifying acceptable limits for dimensions and form, guaranteeing dimensional accuracy. You apply tolerance stack-up analysis to identify potential issues where cumulative tolerances could affect assembly fit and function. This process helps you maintain quality, reduce rework, and ensure parts meet design intent. By embedding these tolerances early, you streamline production and improve overall product reliability.
What Software Tools Optimize Geometric Accuracy During Production?
You can optimize geometric accuracy during production by using software tools like parametric modeling programs that allow precise adjustments. These tools enable you to perform geometric validation, ensuring your designs meet strict tolerances before manufacturing. By integrating real-time feedback and automated checks, you catch potential issues early, reducing errors and waste. This proactive approach keeps your project aligned with specifications, ensuring a high-quality, accurate final product.
How Does Geometric Complexity Affect Manufacturing Costs?
When geometric complexity increases, your manufacturing costs go up because it complicates manufacturing logistics and quality control. More intricate designs require advanced tools, longer production times, and higher precision, all impacting cost estimation. You’ll need to plan for additional resources and potential rework, which can strain budgets. Simplifying geometry helps streamline production, reduce costs, and improve efficiency, making your manufacturing process more predictable and cost-effective.
Conclusion
Think of manufacturing as a grand symphony, where geometry is your guiding melody. Every blueprint, every cut, and every turn follows a precise rhythm that transforms raw materials into masterpieces. With each geometric note played perfectly, your creation comes to life—fluid, harmonious, complete. So, embrace the harmony of geometry in your process; it’s the conductor that guarantees your production sings flawlessly from start to finish.