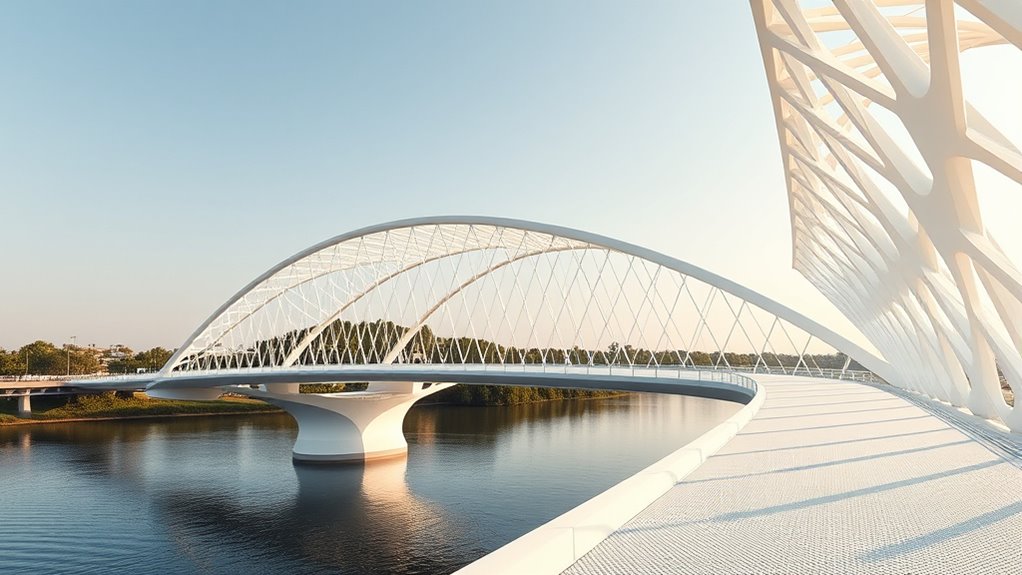
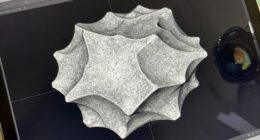
3D-printed bridges highlight how complex geometries can boost engineering strength and flexibility. By using advanced digital design and materials, you can create organic, intricate shapes that optimize force distribution and reduce weight. This approach allows for innovative structures with improved durability, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal. As you explore further, you’ll discover how combining geometry with material science and structural analysis pushes the boundaries of modern bridge design.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing enables complex geometries that optimize strength, weight, and material efficiency in bridge design.
- Advanced computational analysis ensures geometrical forms distribute forces effectively for structural stability.
- Innovative geometries support sustainable and durable structures using novel materials and smart features.
- Additive manufacturing allows for intricate, organic shapes beyond traditional construction limits.
- Geometry-driven design enhances performance, resilience, and customization in 3D-printed bridges.
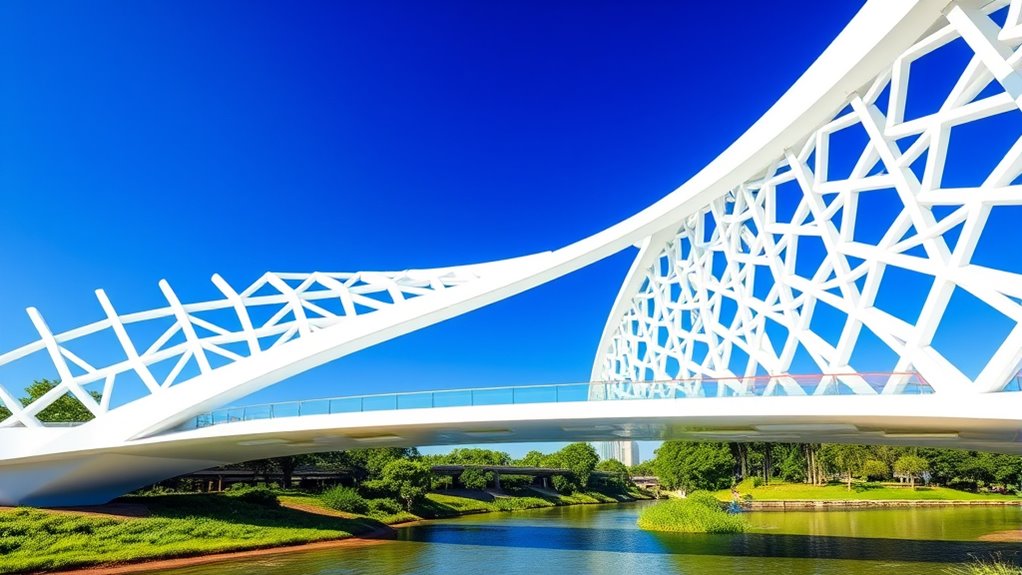

Innovative engineering has made it possible to construct bridges using 3D printing technology, revolutionizing the way we approach infrastructure development. This breakthrough isn’t just about speed or cost savings; it’s about accessing new possibilities in design and material use. When you look at a 3D-printed bridge, you’re witnessing a fusion of materials innovation and structural analysis that pushes the boundaries of traditional construction. In the past, bridges relied heavily on steel and concrete, with limited scope for customization. Now, with 3D printing, you can experiment with advanced composite materials, lightweight alloys, and even bio-inspired substances that offer strength and flexibility while reducing weight and material waste. Materials innovation plays a pivotal role in this new era. Engineers are exploring novel composites and sustainable materials that can be precisely deposited layer by layer, creating complex geometries that were once impossible to achieve. These materials not only improve durability but also allow for better integration of sensors and smart features, making bridges more resilient and easier to maintain. As you examine a 3D-printed structure, you realize that the choice of innovative materials directly influences the structural analysis process. You must carefully evaluate how these materials behave under load, temperature changes, and environmental stressors. The ability to simulate and analyze these factors digitally means you can optimize the design before any physical construction begins, guaranteeing safety and longevity. Additionally, advances in materials characterization enable engineers to better understand how these new materials perform in real-world conditions, further enhancing the reliability of 3D-printed structures. Structural analysis becomes even more critical when working with intricate geometries enabled by 3D printing. Unlike traditional methods, where repetitive elements and straightforward designs dominate, 3D printing allows for organic, complex forms that maximize strength-to-weight ratios. You need to understand how these geometries distribute forces throughout the structure. Finite element analysis and other computational tools help you predict how the bridge will perform under various conditions, guiding you in refining the design for maximum efficiency. This precise analysis ensures that every curve, void, and reinforcement aligns with the engineering principles of stability and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Materials Are Used in the 3D Printing Process?
You use materials like concrete, plastics, or metals in the 3D printing process. These materials are chosen based on their material properties, such as strength, flexibility, and durability. Different printing techniques, like FDM or selective laser melting, require specific materials to achieve ideal results. By selecting the right materials, you guarantee your 3D-printed structures are strong and reliable, making the most of the technology’s potential.
How Long Does It Take to Print the Bridge?
You watch as the printer’s nozzle glides smoothly, layering material with precision. The printing duration for the bridge typically spans several days, depending on its size and complexity. This project timeline allows the printer to meticulously build each segment, like weaving a giant fabric of innovation. Patience pays off, as the end result showcases engineering’s future—strong, lightweight, and crafted through the magic of additive manufacturing.
What Are the Cost Advantages of 3D Printing Bridges?
You’ll find that 3D printing bridges offers significant cost advantages through enhanced cost efficiency and manufacturing savings. This method reduces material waste and minimizes labor costs by streamlining the production process. Plus, it allows for quicker design iterations, cutting down overall project timelines. As a result, you can achieve more affordable construction without compromising quality, making 3D printing a smart choice for innovative and cost-effective infrastructure projects.
How Does the Bridge Withstand Environmental Stresses?
You’ll find that the bridge withstands environmental stresses through effective stress distribution designed into its geometry. The 3D printing process allows engineers to optimize material placement, enhancing environmental resilience against wind, rain, and temperature changes. This tailored stress management helps prevent damage, ensuring durability over time. The innovative design and precise construction work together to keep the bridge strong and resilient, even when faced with challenging environmental conditions.
Can This Technology Be Scaled for Larger Infrastructure Projects?
You can scale this technology for larger projects, but scaling challenges remain. Ensuring structural integrity becomes more complex as size increases, requiring advanced materials and precise engineering. You’ll need to address issues like load distribution and print consistency at larger scales. With ongoing research and development, these hurdles are manageable, making it possible for 3D printing to revolutionize infrastructure by enabling faster, cost-effective, and innovative construction for bigger projects.
Conclusion
As you see this 3D-printed bridge, you realize it’s just the beginning. The power of geometry and innovative technology could redefine engineering as we understand it. But what’s truly coming next? Will future structures challenge what you thought was possible? The potential is limitless, and the next breakthrough might be closer than you think. Stay tuned — the most exciting discoveries are still ahead, and you won’t want to miss what comes next.