In the Artemis moon mission, geometry is essential for guiding your spacecraft from Earth to the lunar surface. It helps plan efficient transfer orbits, accounting for celestial mechanics and gravitational influences of Earth, Moon, and Sun. Precise calculations guarantee smooth orbital insertions and successful landings, allowing adjustments during transit. If you keep exploring, you’ll discover how these complex geometric principles navigate your journey across space and land safely on the Moon.
Key Takeaways
- Geometry helps plan precise transfer orbits between Earth, Moon, and lunar surface, optimizing fuel use and timing.
- It enables accurate lunar landing site selection by analyzing surface features and safe approach angles.
- Orbital mechanics and geometric calculations ensure correct spacecraft trajectory adjustments during transit.
- Geometry guides lunar orbit insertion and surface operations, ensuring safe docking, landing, and rover navigation.
- It facilitates real-time course corrections by interpreting sensor data within celestial coordinate systems.
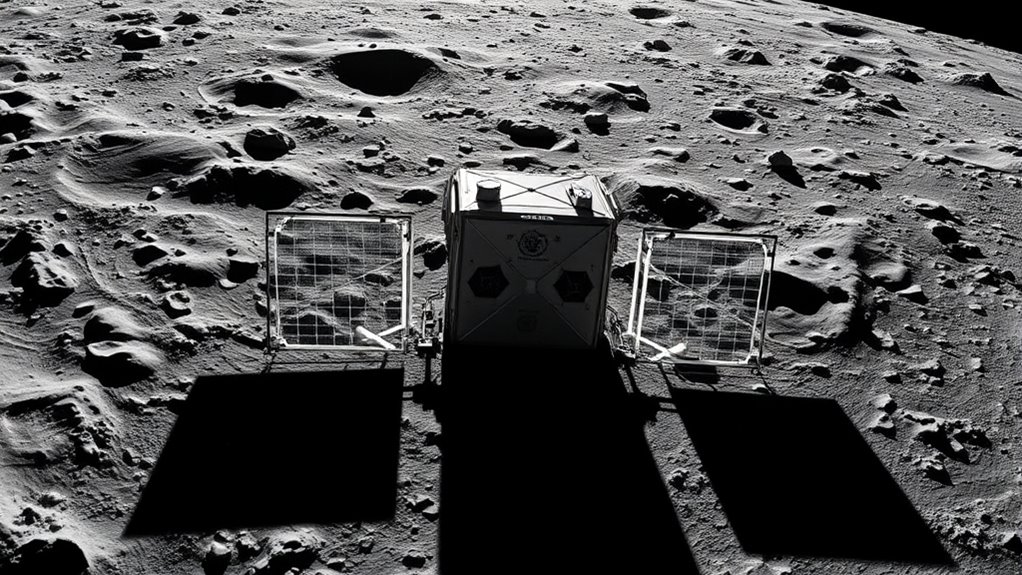
Have you ever wondered how humanity is planning to return to the Moon? It’s not just about rockets and technology; it’s about precise calculations and understanding complex physics. Central to this effort is lunar navigation, which guarantees spacecraft can travel accurately across the vast emptiness of space. When you think about lunar navigation, imagine it as a detailed map combined with a GPS system, guiding astronauts from Earth’s orbit to the lunar surface. Achieving this requires mastery of orbital mechanics, the branch of physics that describes how objects move in space under the influence of gravity. Orbital mechanics allows mission planners to plot the most efficient paths, minimizing fuel consumption and travel time, which are crucial for the success and safety of lunar missions.
The Artemis program relies on advanced models of orbital mechanics to determine the best trajectories for spacecraft. These models consider the gravitational influences of Earth, the Moon, and even the Sun, helping mission teams design precise maneuvers. For example, entering lunar orbit involves complex calculations to ensure the spacecraft slows down just enough to be captured by the Moon’s gravity without crashing or drifting away. This process, called orbital insertion, is carefully timed and executed based on a deep understanding of celestial mechanics. Without this knowledge, even a small miscalculation could lead to mission failure or loss of valuable assets.
Lunar navigation also involves real-time adjustments. Once in transit, spacecraft continuously receive data from onboard sensors and ground-based tracking stations, enabling mission control to make small course corrections. These adjustments are rooted in the principles of orbital mechanics—analyzing the spacecraft’s position, velocity, and the gravitational influences acting upon it—to keep it on the right path. This ongoing process ensures that when the spacecraft reaches the lunar vicinity, it arrives precisely where it needs to be, whether for orbiter deployment, landing, or surface operations. Additionally, understanding celestial geometry is essential for planning precise landing sites and transfer orbits.
Furthermore, as Artemis aims to establish a sustainable presence on the Moon, understanding orbital mechanics becomes even more crucial. It enables the planning of lunar landings at ideal locations, ensuring safety and accessibility for future missions. It also helps in designing transfer orbits for lunar rovers and habitats, making sure they can reach various parts of the lunar surface efficiently. In essence, the success of Artemis hinges on the mastery of celestial geometry, where every trajectory is a carefully calculated dance guided by the laws of orbital mechanics. This science is what turns ambitious lunar exploration into a precise, achievable reality, guiding humanity’s return to the Moon with confidence and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Geometric Modeling Improve Lunar Surface Navigation?
Geometric modeling improves lunar surface navigation by enabling you to analyze geometric data and recognize surface features accurately. It helps you create detailed maps, identify landmarks, and understand terrain variations, making navigation safer and more precise. By using geometric data analysis, you can plan ideal routes, avoid hazards, and guarantee successful exploration. Surface feature recognition, integrated into the models, further enhances your ability to navigate confidently across the moon’s challenging landscape.
What Role Does Geometry Play in Lunar Landing Site Selection?
Did you know that precise geometry helps scientists select ideal lunar landing sites with 3D models? You see, understanding lunar gravity and surface features through geometric analysis ensures safer landings. By using geometric measurements, engineers identify flat, stable terrain away from hazards, much like a space station’s accurate positioning. This careful planning maximizes safety and mission success, guiding you to the most suitable spots on the Moon’s surface.
How Are Geometric Algorithms Used in Spacecraft Trajectory Planning?
You use geometric algorithms in spacecraft trajectory planning by analyzing satellite tracking data and applying principles of orbital mechanics. These algorithms help you optimize paths, ensuring fuel efficiency and precise landings. By calculating the angles, velocities, and positions, you can adjust trajectories in real-time, avoiding obstacles and ensuring safety. This process allows you to accurately navigate through space, leveraging geometry to guide your spacecraft on its lunar journey.
What Geometric Tools Assist Astronauts During Moon Surface Operations?
During moon surface operations, you rely on geometric tools like robotic precision and structural design to guarantee safety and accuracy. These tools help you navigate challenging terrain, avoid hazards, and perform tasks with high accuracy. Robotic precision allows you to make fine adjustments, while structural design provides stability and support. Together, they guide your movements and decisions, enabling successful exploration and scientific work on the lunar surface.
How Is Lunar Topography Mapped Using Geometric Techniques?
You map lunar topography using geometric techniques by analyzing crater shapes and distributions through crater analysis, which reveals surface ages and features. Elevation mapping employs triangulation and laser scanning data to create precise 3D models of the terrain. These methods allow you to understand surface variations, plan landing sites, and navigate safely, ensuring successful moon surface operations by leveraging geometry to interpret and visualize the lunar landscape accurately.
Conclusion
As you follow the Artemis Moon Mission, you’ll see how geometry acts like a guiding star, steering humanity’s greatest leap. Just as a compass points true north, precise calculations guarantee safe landings and successful journeys. With each step, you realize that math isn’t just numbers—it’s the blueprint for exploration. Together, you’re witnessing how geometry transforms dreams into reality, lighting the path forward as boldly as the moon itself shines in the night sky.