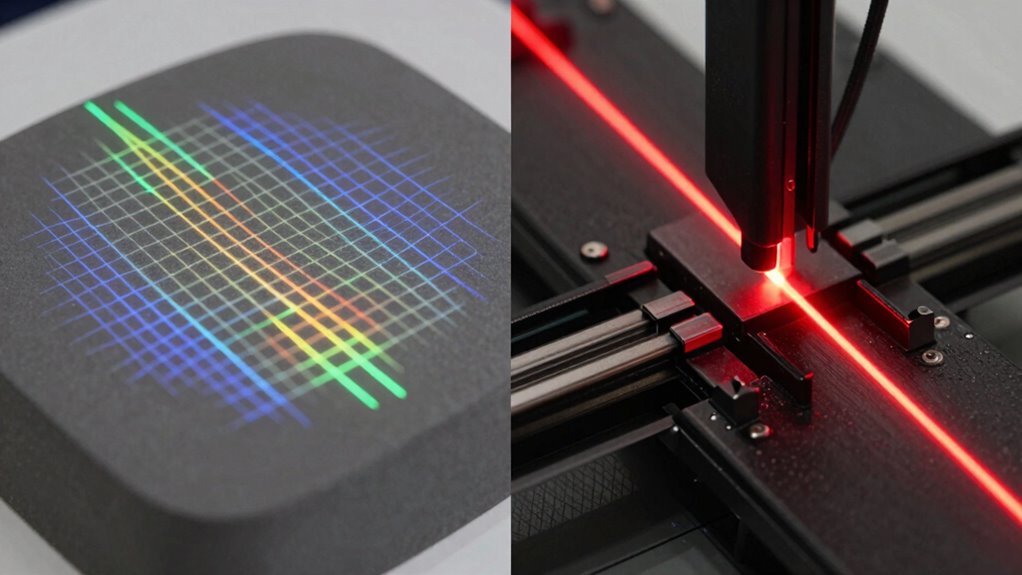
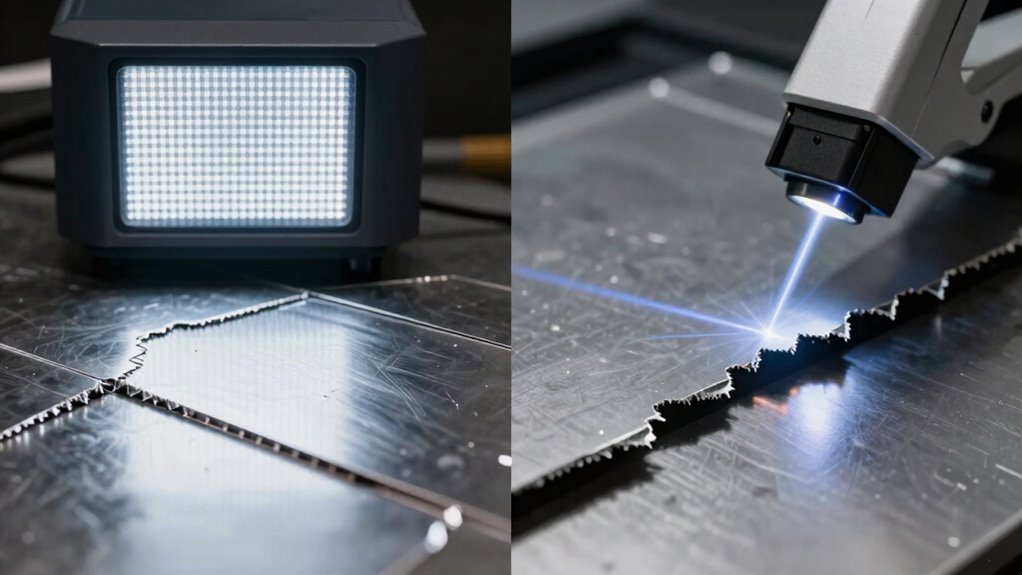
If you’re comparing structured light and laser line scanners for edge capture, laser line scanners generally do a better job. They produce sharper, more precise edges, especially on complex or reflective surfaces. Structured light scanners rely on pattern distortion, which can sometimes result in blurry or less defined edges, especially under certain conditions. To discover more about which type suits your needs best, consider how each system handles surface details and environmental factors.
Key Takeaways
- Laser line scanners produce sharper, more precise edges, especially on complex or reflective surfaces, due to focused laser beams.
- Structured light scanners rely on pattern deformation analysis, which can result in less defined edges under certain conditions.
- Higher sensor resolution in both systems improves the detection of fine edges, but laser scanners generally maintain edge clarity better.
- Laser scanners excel in challenging environments with surface reflectivity or uneven textures, ensuring more accurate edge capture.
- For capturing intricate surface details and subtle edges, laser line scanners are typically more reliable than structured light scanners.
Which 3D Scanner Is Best for Edges and Fine Details?
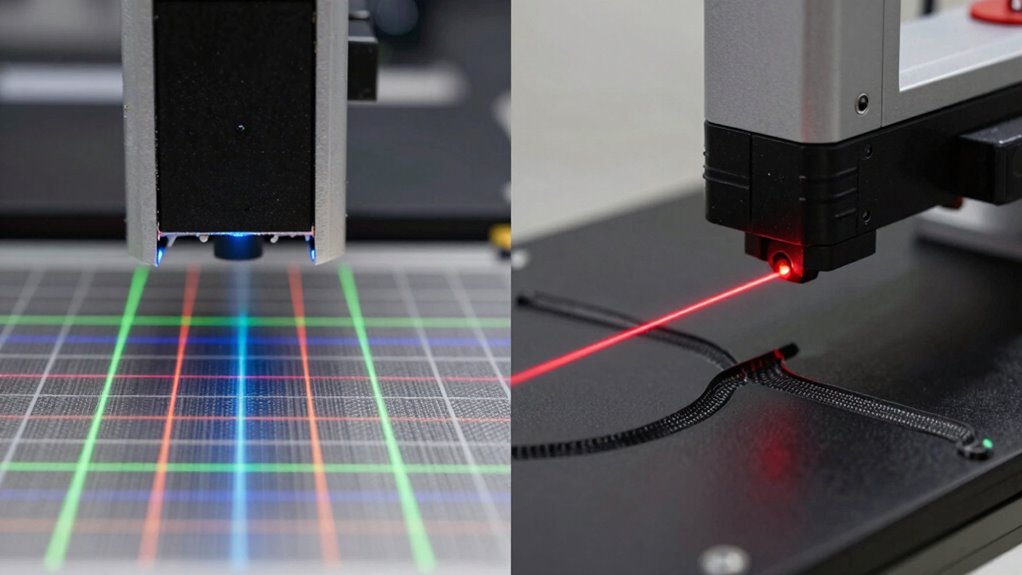
When it comes to capturing edges and fine details, choosing the right 3D scanner makes all the difference. For tasks requiring high scanning accuracy, laser line scanners excel because they produce precise, consistent data even on complex geometries. They’re particularly effective at capturing sharp edges and intricate features, thanks to their focused laser beams. Surface reflectivity can influence results; highly reflective or shiny surfaces may cause glare, reducing accuracy unless you apply surface treatment or use specialized settings. Surface reflectivity can significantly impact scanning performance; in some cases, applying a matte spray can improve results with reflective surfaces. Moreover, application environments such as lighting conditions and surface textures can significantly impact scanning performance. Ultimately, if edge detail and accuracy are your priorities, laser line scanners typically provide superior results, especially when surface conditions are challenging. Additionally, innovative European cloud servers can enhance data processing and storage efficiency for 3D scanning workflows.
How Do Structured Light Scanners Capture Edges?
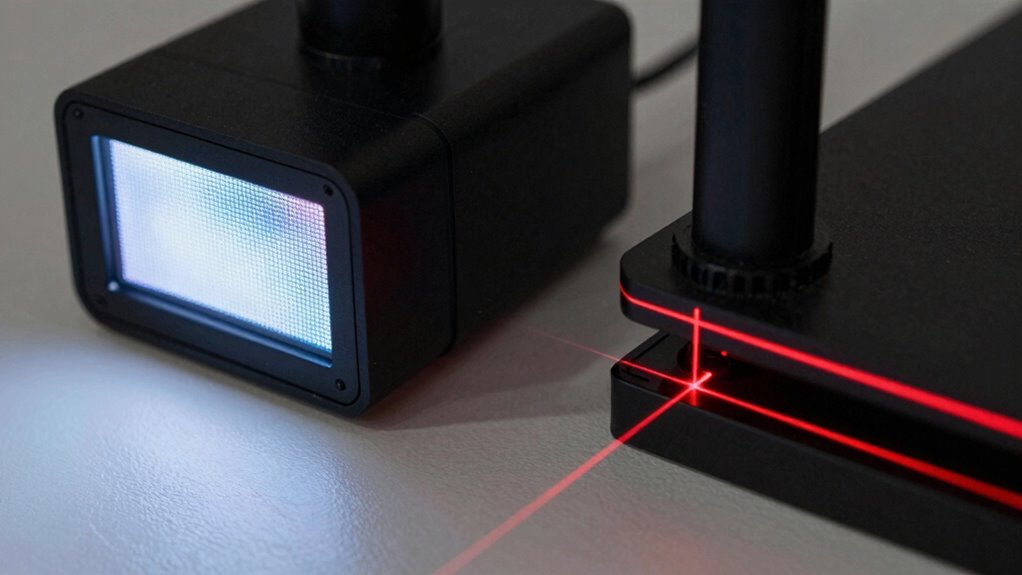

Structured light scanners use edge detection techniques to identify where surfaces change abruptly. They project patterns that, when distorted by edges, reveal critical data through advanced processing algorithms. These combined methods enable precise capturing of edges and fine details in complex shapes. Additionally, sensor accuracy plays a vital role in how effectively these scanners can record intricate details and subtle surface variations. The integration of digital resources and ongoing support helps optimize the use of these advanced scanning systems.
Edge Detection Techniques
Edge detection in structured light scanners relies on projecting precise patterns onto the object and analyzing how these patterns deform. When light hits the surface, light scattering occurs, affecting how the pattern appears. Areas with sharp edges cause distinct deformations, making edges easier to identify. The pattern complexity plays a vital role; simple patterns may not reveal subtle edges, while more intricate patterns enhance contrast at boundaries. By examining the deformation and distortions in the projected pattern, your scanner can accurately detect edges, even in complex geometries. This method allows for high-resolution edge detection, as the patterns are tailored to maximize contrast at edges. Overall, the combination of pattern projection and analysis of light scattering enables structured light scanners to capture edges precisely and reliably.
Pattern Projection Methods
Pattern projection methods are central to how structured light scanners detect edges. You use a projector to cast specific patterns—such as grids, stripes, or dots—onto the object’s surface. These patterns deform when they hit edges or surface irregularities, causing distortions that the scanner’s cameras capture. By analyzing these distortions, the scanner performs edge detection, pinpointing where the surface changes sharply. The pattern projection allows for precise identification of edges, especially in complex geometries. Different projection methods, like binary codes or color patterns, enhance the accuracy of edge detection. This technique guarantees that the scanner captures detailed surface features, making it highly effective for detailed 3D reconstruction. Ultimately, the pattern projection method is essential for accurate edge detection in structured light scanning.
Data Processing Algorithms
Once the patterned light is projected onto the object, the scanner’s cameras capture the distorted images. These images contain raw data that require processing to accurately identify edges. You use advanced algorithms, often leveraging machine learning, to analyze and interpret the data. Noise filtering plays a vital role here, removing irrelevant or misleading information caused by surface reflections or environmental factors. Machine learning models can improve edge detection by learning from previous scans, enhancing accuracy over time. This combination helps you distinguish true edges from noise, ensuring precise surface detail capture. The processed data then generates a detailed 3D model, with sharp edges and accurate contours. Efficient data processing algorithms are essential for transforming raw captured images into reliable, high-quality 3D representations.
How Do Laser Line Scanners Detect Tiny Details?
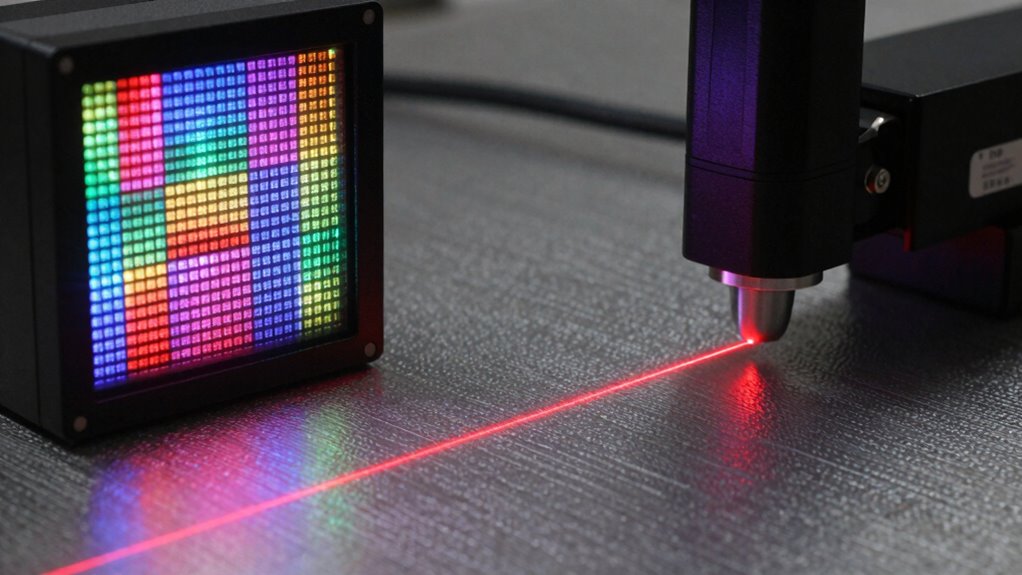
Laser line scanners detect tiny details through precise light reflection, which allows them to pick up even the smallest surface features. However, their effectiveness depends on sensor resolution limits, which can restrict the level of detail captured. Sensor resolution is a critical factor that influences the accuracy and detail of scans. Understanding these factors helps you optimize scanning accuracy for your specific needs. Accurate data collection is essential for ensuring reliable results in various applications.
Light Reflection Precision
Laser line scanners achieve remarkable detail by meticulously measuring how light reflects off tiny surface features. Their ability to detect small details depends on understanding light scattering and surface reflectivity. When laser light hits a surface, variations in reflectivity influence the reflected signal, revealing minute features. Smooth, highly reflective surfaces return cleaner signals, while rough or matte surfaces cause scattering, reducing precision. To optimize detection, scanners adjust laser intensity and angle, minimizing the effects of scattering. The following table illustrates key factors influencing light reflection precision:
| Surface Properties | Impact on Reflection |
|---|---|
| High reflectivity | Clear, accurate readings |
| Low reflectivity | Increased scattering, less detail |
| Surface Texture | Effect on Light Reflection |
| Smooth | Consistent reflection |
| Rough | Scattered light, detail loss |
| Matte | Diffused reflection, reduced clarity |
Sensor Resolution Limits
Sensor resolution sets the fundamental limit on how small a detail a laser line scanner can detect. Your scanner’s sensor limitations determine the smallest features it can accurately capture. Higher resolution sensors can detect tinier edges and surface variations, but they also face resolution challenges, such as increased data processing and potential noise. When scanning complex or fine details, if your sensor’s resolution isn’t sufficient, critical edges may blur or be missed altogether. This means that even with precise laser projection, your scanner’s ability to capture tiny details depends on its sensor’s capability. To maximize detail detection, choose a scanner with an appropriate resolution for your application, and be aware that resolution limits can restrict the level of detail you can reliably record. Sensor resolution directly influences the scanner’s capacity to identify minute surface features.
Comparing Edge Accuracy in Structured Light and Laser Line Scanners
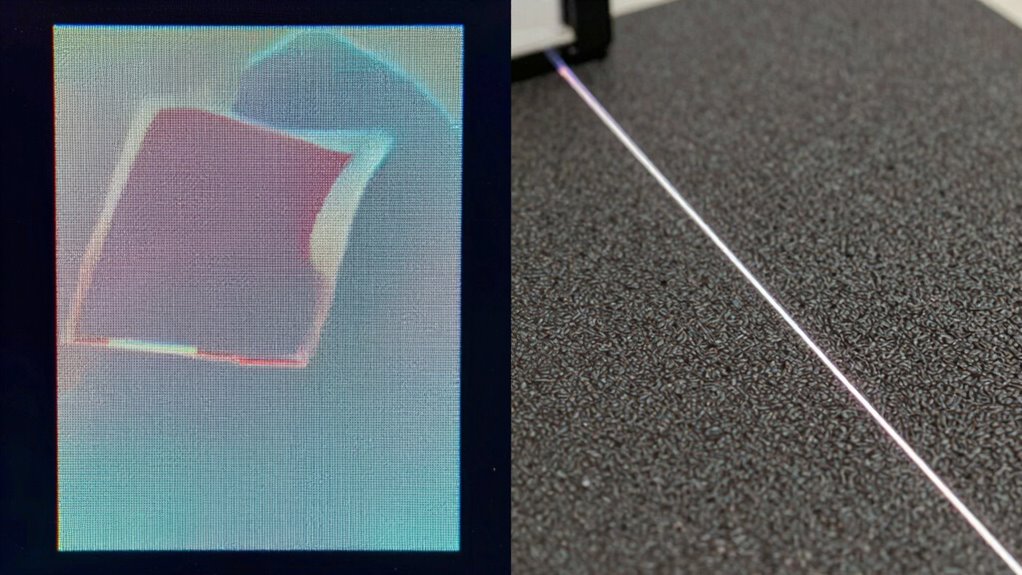
When evaluating edge accuracy, structured light and laser line scanners each have distinct strengths that influence their performance. Structured light scanners excel in capturing edges with high contrast, especially on surfaces with consistent reflectivity. They can distinguish subtle changes in edges, but surface reflectivity variations can reduce accuracy. Laser line scanners, on the other hand, produce sharp, precise lines that often better detect edges on reflective or uneven surfaces. Their ability to maintain edge contrast under challenging conditions makes them ideal for detailed edge capture.
- Feel confident knowing your scanner can handle complex surfaces
- Trust in sharp, clear edge detection for precise modeling
- Overcome surface reflectivity challenges with the right technology
- Achieve accurate edges that elevate your project quality
How Does Scan Resolution Affect Edge and Detail Capture?
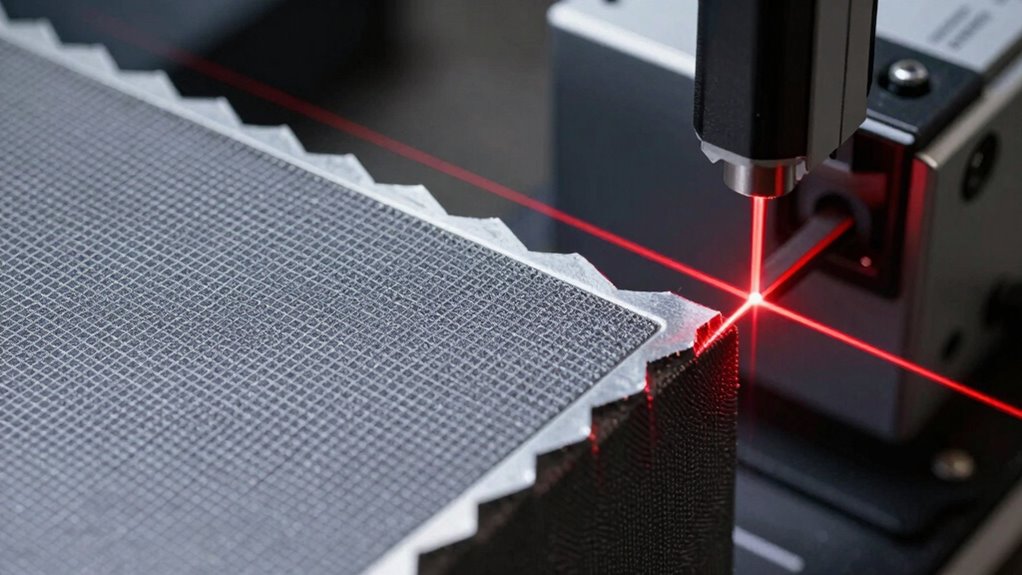
Higher scan resolution directly enhances your ability to capture fine edges and intricate details, making your 3D models more accurate and realistic. The resolution impact determines how clearly small features and subtle textures are recorded, reducing the need for post-processing corrections. With higher resolution, you’ll notice an improvement in detail enhancement, capturing even the tiniest grooves or surface irregularities. This is especially important when scanning complex geometries or objects with delicate features. However, increasing resolution also means longer scan times and larger data files, so balance is key. Ultimately, a higher resolution gives you a more faithful digital representation, ensuring that edges are sharp and details are well-preserved. This makes your scans more precise and reliable for detailed analysis or reproduction.
Best Uses of Each Scanner for Complex Geometries
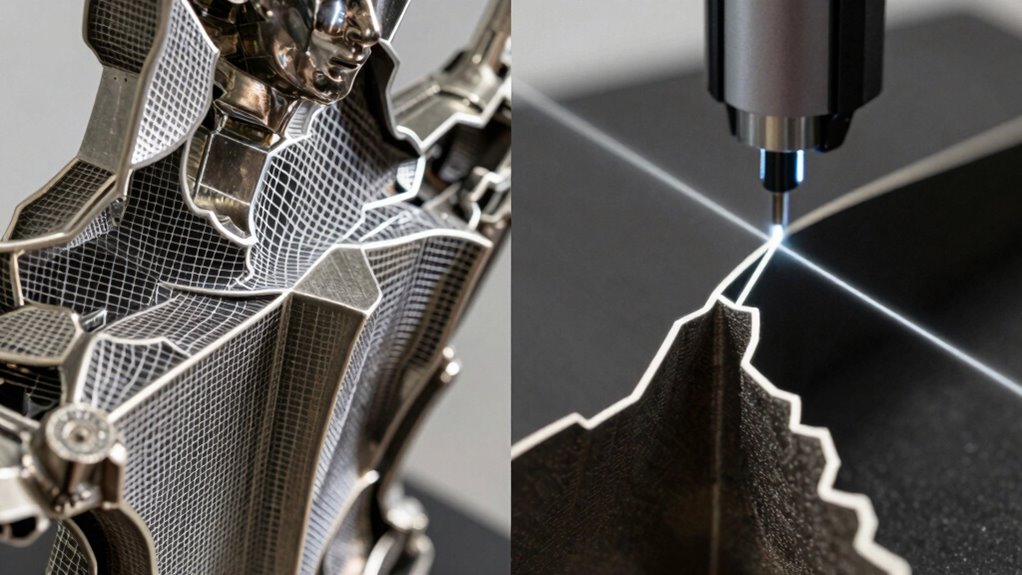
Structured light scanners excel at capturing complex geometries with intricate surface details because they project precise patterns onto objects to generate accurate 3D models. They’re ideal when you need high texture fidelity and color accuracy to preserve fine surface nuances. Use them for detailed sculptures, heritage artifacts, or intricate machinery where every surface detail matters. They excel at capturing subtle curves, sharp edges, and textured surfaces with clarity.
Structured light scanners capture intricate surface details with high accuracy and vibrant color.
- Achieve stunning surface detail with true color representation
- Perfect for capturing delicate textures and fine features
- Maintain high accuracy in complex, multi-layered geometries
- Bring intricate designs to life with sharp edges and detailed contours
If your project demands precise surface information and vibrant color, structured light scanners are your best choice. They excel at revealing the beauty and complexity of detailed, textured surfaces.
What Are the Main Limitations in Edge Precision?
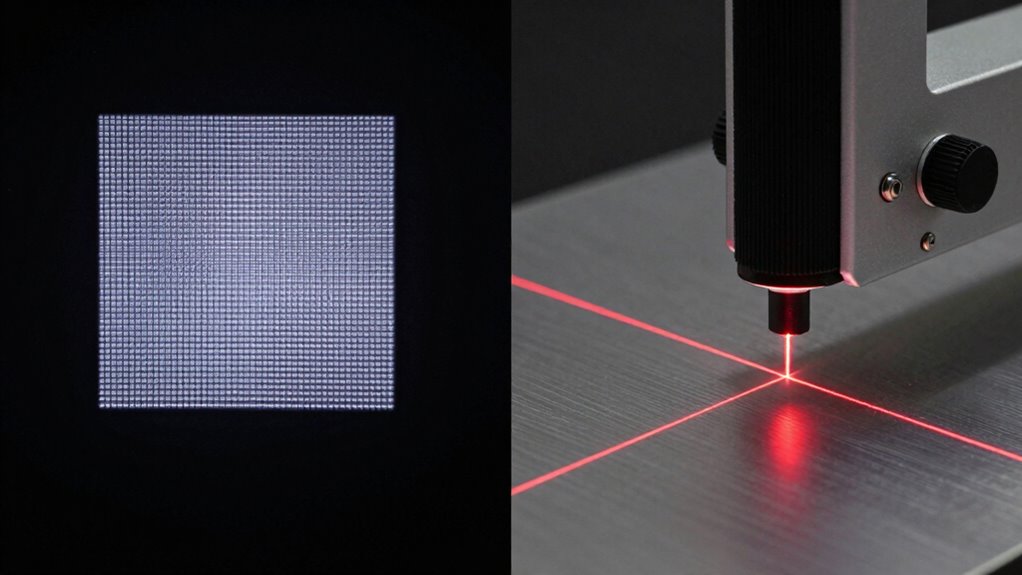
Edge precision remains a challenge for structured light scanners because their projection patterns can struggle to accurately capture sharp corners and fine details. This often results in edge distortion, where edges appear blurry or less defined. Such distortions directly impact measurement accuracy, especially on complex geometries with intricate features. The limited resolution of structured light systems can cause the scanner to interpolate or smooth out edges, reducing the fidelity of the data. Additionally, surface reflectivity and ambient light conditions can further impair edge detection. You might notice that capturing crisp edges requires careful calibration and ideal setup, but some limitations remain inherent to the technology. Overall, these factors limit the ability of structured light scanners to precisely record edges, especially when high detail and accuracy are critical. Understanding sensor limitations can help optimize scanning strategies for better edge capture.
How Can You Improve Edge Detail Capture? Tips for Each Scanner Type
To enhance edge detail capture, start by optimizing your scanner’s position to get the best angle and coverage. Adjust your projector settings to improve contrast and resolution, making edges clearer. Additionally, refine your data processing techniques to better handle complex details and reduce noise in your scans. Incorporating Free Floating techniques can also improve the flexibility and accuracy of your scanning process, especially in irregular environments.
Optimize Scanner Positioning
Optimizing scanner positioning is essential for capturing detailed edges accurately, and the approach varies depending on the scanner type. To get the best results, consider how lighting conditions impact your scan, as glare or shadows can obscure edges. Confirm calibration procedures are up-to-date, so your scanner maintains accuracy. Adjust the scanner’s angle to maximize edge visibility, avoiding angles that cause reflections or distortions. Keep the scanner steady to prevent blurring and ensure consistent data capture. Proper positioning helps you reveal intricate details, making your scans more precise and reliable.
- Feel confident in your setup, knowing you’re capturing every edge perfectly
- Minimize errors caused by improper angles or lighting
- Unlock the scanner’s true potential with precise positioning
- Achieve flawless scans that impress every time
Adjust Projector Settings
Adjusting projector settings is essential for capturing fine edge details, and the specific approach depends on your scanner type. Proper projector calibration guarantees accurate light projection, which improves edge clarity. Adjust light intensity carefully: too bright can cause glare, while too dim reduces detail. For structured light scanners, focus on refining the calibration to enhance surface coverage. Laser line scanners benefit from tuning light intensity to highlight edges without overwhelming the sensor. Use the following tips:
| Scanner Type | Calibration Focus | Light Intensity Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Light | Precise projector alignment | Moderate brightness for detail |
| Laser Line | Fine-tune laser focus | Adjust to avoid overexposure |
| Both | Regular calibration checks | Balance for ideal edge detection |
Additionally, maintaining consistent calibration routines ensures sustained edge detection performance over time. Regularly verifying your setup and adjusting for environmental changes can further improve edge detection accuracy. Incorporating proper maintenance practices can also help sustain optimal scanner performance and edge capture quality.
Enhance Data Processing Techniques
Enhancing data processing techniques is essential for capturing sharper edge details in both structured light and laser line scanning. To improve accuracy, focus on advanced calibration to align your scanner’s components precisely, minimizing measurement errors. Implement noise reduction algorithms to eliminate unwanted data that obscures fine edges, leading to clearer results.
Consider these strategies:
- Use high-quality filters to sharpen edge detection
- Apply advanced calibration routines regularly
- Utilize software with noise suppression capabilities
- Refine data algorithms to enhance edge contrast
Choosing Based on Cost, Speed, and Usability
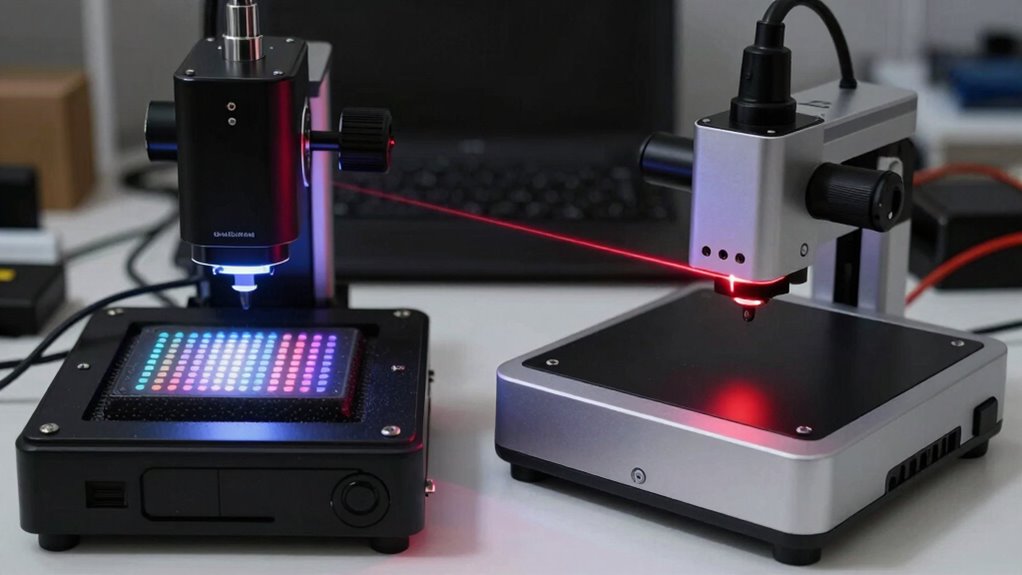

When choosing between structured light and laser line scanners, cost, speed, and usability are key factors that can considerably influence your decision. Conducting a thorough cost comparison helps determine which scanner fits your budget, as structured light systems often have higher upfront costs but may offer quicker setup and operation. Usability factors, like ease of calibration, user interface, and portability, also play a crucial role. If you need fast, straightforward operation with minimal training, one system might stand out over the other. Laser line scanners tend to be more durable in challenging environments, which can impact usability. Additionally, considering accuracy and precision of the scanner can help ensure you select a device that captures edges accurately and reliably. Evaluating the ease of setup can further streamline your workflow and reduce the learning curve. Incorporating environmental resilience into your assessment can also be critical, especially in demanding conditions. Understanding the technology differences between the systems can help you make a more informed decision that aligns with your project needs. Ultimately, balancing your budget with your project’s timeline and ease of use will guide you toward the most practical choice for your specific needs.
Which Scanner Performs Best for Edges and Fine Features?
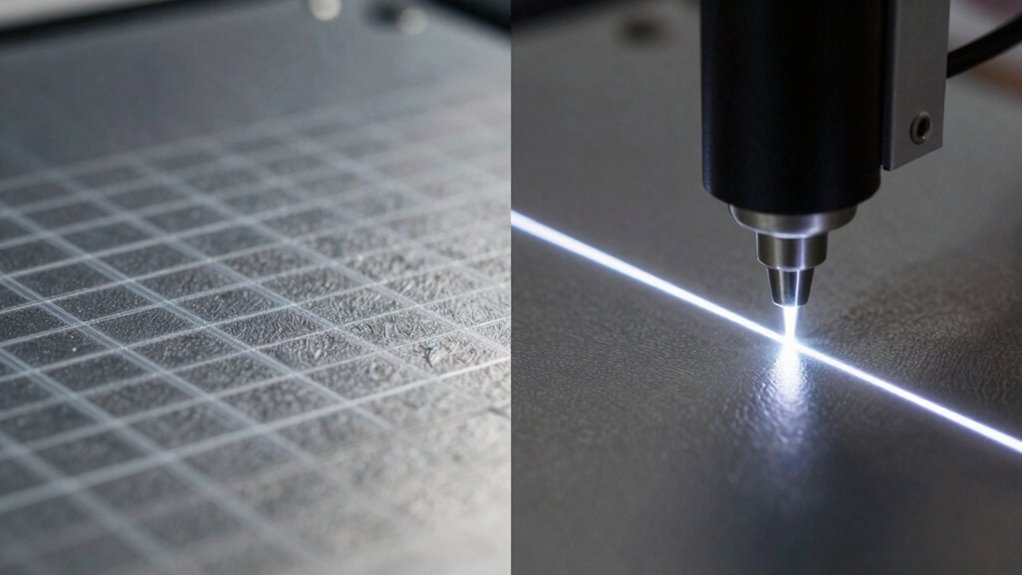
Choosing the right scanner for capturing edges and fine details depends largely on the technology’s ability to resolve small features accurately. Laser line scanners excel in this area, providing superior edge enhancement and precise feature extraction. They can detect subtle variations, making sharp edges and intricate details stand out clearly. Structured light scanners may struggle with tiny features but are excellent for capturing broader surfaces quickly. When selecting a scanner, consider how well it preserves fine features without losing critical edge information. The best scanner for edges and fine features will:
- Deliver crisp, well-defined edges
- Enhance subtle surface transitions
- Capture intricate details with accuracy
- Support reliable feature extraction for detailed models
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Environmental Factors Influence Edge Accuracy in Each Scanner Type?
Environmental factors like ambient interference and surface reflectivity can impact edge accuracy in both scanner types. You might notice that ambient light causes noise, reducing precision, especially for laser line scanners. Similarly, highly reflective surfaces can distort data for structured light scanners. To improve accuracy, you should control lighting conditions, use surface treatments, or adjust scanner settings to minimize these effects, ensuring sharper edge detection and reliable measurements.
Can Post-Processing Software Enhance Edge Detail Quality After Scanning?
Yes, post-processing software can considerably enhance edge detail quality after scanning. By adjusting scan resolution and applying advanced software algorithms, you can sharpen edges, fill gaps, and improve overall accuracy. These tools help refine raw data, reducing noise and smoothing imperfections. So, after scanning, don’t hesitate to use specialized software to optimize your scans and achieve crisper, more precise edge details.
What Maintenance Routines Are Recommended to Preserve Edge Capture Precision?
You should calibrate your scanner regularly, ideally before each major use, to maintain edge capture precision. Applying protective coatings to the scanner’s lens or sensor helps prevent dust, scratches, and damage that can degrade accuracy. Additionally, keep the equipment clean and store it in a controlled environment. Following a consistent maintenance routine guarantees your scanner delivers precise edge details and prolongs its lifespan.
Are There Specific Material Properties That Affect Edge Detection Capabilities?
A picture is worth a thousand words, and the same applies to edge detection. Your scanner’s ability to capture edges depends on material reflectivity and surface texture. Highly reflective surfaces can cause glare, obscuring edges, while rough textures scatter light, improving detection. To optimize accuracy, consider coating shiny materials or smoothing textured surfaces. Understanding these properties helps you choose the right scanner settings and achieve precise edge capture every time.
How Does Operator Skill Impact Edge and Fine Detail Scanning Outcomes?
Your operator training and scanning technique greatly impact edge and fine detail capture. When you understand proper setup, such as ideal positioning and lighting, you improve accuracy. Skilled operators adjust scanning parameters for different materials and surfaces, reducing errors. Consistently practicing good scanning techniques helps you better capture intricate edges and details, ensuring high-quality results. Investing in training enhances your ability to use each scanner’s strengths effectively, leading to more precise, detailed scans.
Conclusion
Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, and the right scanner makes those words clearer. If you need pinpoint accuracy for tiny edges, laser line scanners often lead the way. But if speed and ease matter more, structured light scanners can still deliver impressive detail. Ultimately, choosing the best tool depends on your needs. As they say, “You get what you pay for”—so pick wisely to capture every edge and detail perfectly.